“
In today's world, sugary beverages like soda, energy drinks, and sweetened juices have become ubiquitous, offering a quick fix of sweetness and energy. However, beneath their enticing taste lies a host of health risks that can profoundly impact our well-being. Join us as we explore why these beverages are more than just a guilty pleasure—they're a serious concern for public health.1
1
”
Sugary drinks significantly contribute to obesity due to their high-calorie content and lack of essential nutrients. Regular consumption can lead to weight gain and elevate the risk of diabetes and heart disease. 1
High sugar intake from sugary beverages can result in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Managing diabetes requires significant lifestyle changes and can lead to serious complications, including nerve damage and cardiovascular issues. 2
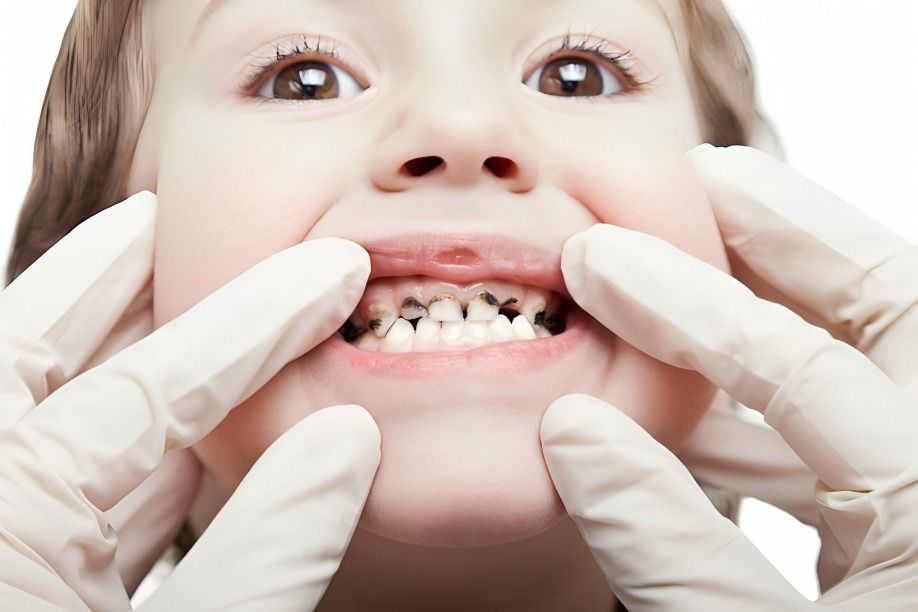
The sugars in sugary drinks fuel bacteria that produce acids, leading to tooth enamel erosion and cavities. Maintaining good dental hygiene and limiting sugary drink consumption are essential for preventing oral health issues.
Excessive sugar consumption can cause fatty liver disease. This condition, if left untreated, can progress to more severe liver problems. Addressing sugar intake through diet and lifestyle changes is crucial for maintaining liver health. 3
Sugary beverages can raise cholesterol levels and blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart disease. Reducing sugary drink consumption can help improve cardiovascular health and lower these risks. 4
High sugar and fructose content in sugary drinks can contribute to the formation of kidney stones. Staying hydrated and cutting back on sugary beverages can help prevent kidney stones. 5
Sugary beverages can interfere with calcium absorption, leading to weakened bones and a higher risk of osteoporosis. Ensuring adequate calcium intake and maintaining bone health are essential for preventing bone-related issues.6
Excess sugar intake is linked to impaired cognitive function and an increased risk of dementia. A balanced diet low in sugars supports brain health and cognitive function. Eating a variety of nutrients helps maintain mental acuity. 7
Rapid fluctuations in blood sugar levels from sugary drinks can lead to mood swings and irritability. Keeping blood sugar levels stable is important for mental well-being and emotional stability. 8
Sugary beverages can be addictive due to their effect on dopamine levels in the brain. This addiction can lead to cravings. Managing intake and finding healthier alternatives can help overcome sugar dependence. 9
Regular consumption of sugary drinks can disrupt gut flora and contribute to digestive issues such as bloating and discomfort. Maintaining a balanced diet with fiber-rich foods supports healthy digestion. 10
High sugar intake is associated with an increased risk of certain cancers. Choosing a diet low in sugars may help reduce cancer risk. Consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall health and cancer prevention. 11
Sugary beverages provide empty calories and can displace nutrient-dense foods in the diet, potentially leading to nutrient deficiencies. Ensuring a well-balanced diet with essential vitamins and minerals supports overall health and nutrition. 12
Excessive sugar consumption can disrupt insulin and hunger-regulating hormones, contributing to metabolic imbalances. Managing sugar intake helps maintain hormonal balance and metabolic health. 13
Sugar consumption from sugary beverages can worsen skin conditions like acne and accelerate skin aging. A diet low in sugars, combined with proper skincare, supports healthier skin. Drinking plenty of water and eating antioxidants are also beneficial. 14
High sugar intake has been linked to an increased risk of age-related macular degeneration, affecting vision in older adults. Reducing sugar intake and consuming eye-friendly nutrients can help protect vision. 15
The production and disposal of sugary beverages contribute to environmental pollution and waste. Reducing the consumption of these beverages helps minimize environmental impact. 16
The marketing and availability of sugary drinks can contribute to health disparities, especially in low-income communities. Promoting healthier choices and improving access to nutritious options helps address these disparities. 17
Consuming high amounts of sugar can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections and illnesses because excessive sugar can reduce the efficiency of white blood cells. 18
Sugar molecules can attach to proteins in the body through a process called glycation, forming harmful compounds known as Advanced Glycation End-products (AGEs). 19


