“
Trade and exchange in the Neolithic era marked a transformative period in human history, facilitating connections between communities and fostering economic growth. This blog delves into 20 facts about trade and exchange in the Neolithic era, highlighting how early humans shared resources, ideas, and innovations. From the barter system to the exchange of agricultural products, these interactions shaped social structures and laid the groundwork for future economies. Join us as we explore the significance of trade and exchange during this pivotal time and uncover how it influenced the development of early societies.1
”
Neolithic trade networks were remarkable, connecting distant communities. Farmers exchanged pottery, tools, and food, forging relationships and cultural connections that laid the foundation for future societies.1
Obsidian was the ultimate treasure of the Neolithic, prized for tool-making. Its trade showcased early artisans’ skills and underscored the importance of specialized craftsmanship in thriving communities.2
Salt, essential for food preservation, was a highly sought-after commodity. Neolithic people traded it extensively, enhancing their diets and highlighting early economic strategies and interdependence.3
Surplus crops revolutionized Neolithic economies. With abundant food, communities traded for tools and crafts, creating a vibrant exchange culture and pioneering the concept of specialized labor.4
Trade elevated social hierarchies, granting wealth and status to those involved. This shift led to pronounced social stratification, reshaping community dynamics and influencing societal development over time.5
Neolithic people cherished decorative items like beads, which were commonly traded. These artifacts reflected personal identity and status, revealing the cultural significance of adornment in early societies.6

Granaries were communal treasures in Neolithic villages, allowing storage of surplus grains. This collaboration enhanced trade opportunities and fostered cooperation among neighboring communities, solidifying social bonds.
Art often depicted trade scenes, highlighting its importance. Neolithic artists celebrated commerce, emphasizing the relationships formed through exchange and the integral role it played in daily life.7
Non-local pottery styles revealed cultural exchange among Neolithic communities. This sharing of artistic techniques enriched traditions, expanding cultural horizons and fostering a collective identity.8
Trade routes thrived along rivers, guiding Neolithic commerce. These natural pathways facilitated exchanges, showcasing how early people adapted their trade practices to their landscapes and resources.9
Some settlements became bustling trading hubs, attracting diverse groups. These centers sparked cultural interactions, blending goods and ideas that shaped the trajectory of human civilization.10
Trade included rituals, strengthening community bonds. Exchanges were not mere transactions; they forged trust and cooperation, creating shared identities that contributed to cultural cohesion.11
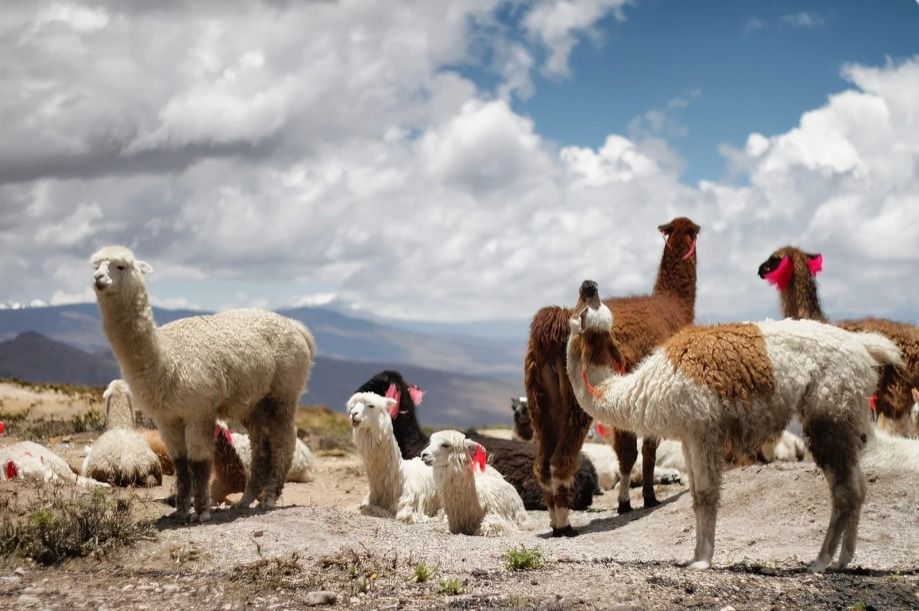

Domesticated livestock, especially sheep and goats, were trade staples. These animals provided essential resources, reinforcing their value in exchange networks and transforming the Neolithic economy.
Gatherings for trade fairs were vibrant community events. These occasions encouraged social interaction and cultural exchange, allowing Neolithic people to celebrate their shared identities through commerce.12
The Neolithic diet blossomed through trade, introducing grains and legumes. This diversity improved nutrition, demonstrating early humans’ understanding of the value of varied food sources.13
Specialized tools, like grinding stones, transformed agriculture. Traded among communities, these innovations exemplified the interconnectedness of Neolithic economies and the exchange of practical knowledge.14
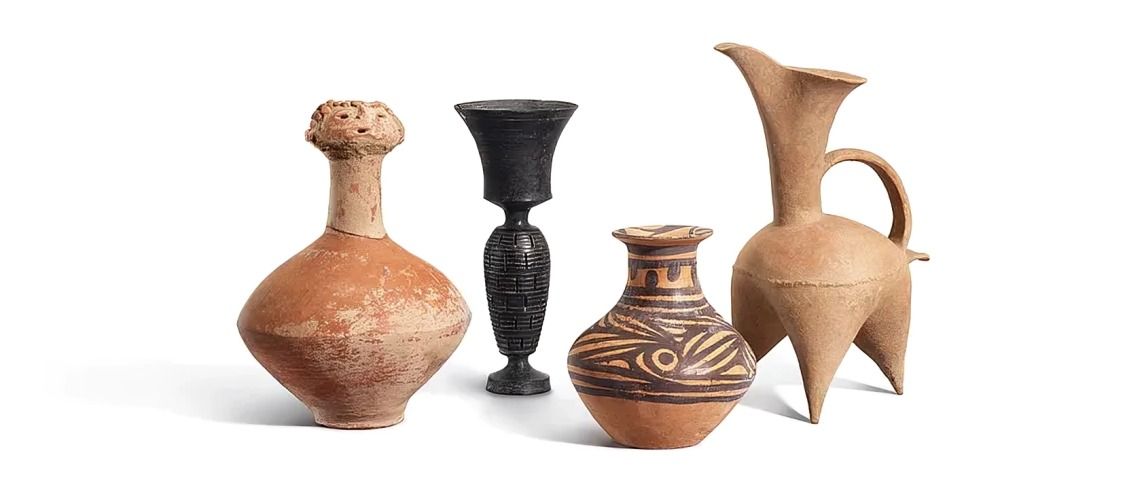

Certain regions gained fame for unique products, such as pottery. This specialization not only fueled trade but also sparked local pride, driving artisans to innovate and excel.
Exotic materials like amber and lapis lazuli captivated Neolithic traders. These luxurious goods represented wealth and status, revealing far-reaching trade networks that linked diverse cultures.15
Knowledge exchange was invaluable in Neolithic times. Sharing agricultural techniques and animal husbandry practices shaped societal advancements and enhanced food production, showcasing the power of information.16
The legacy of Neolithic trade forged the path for future civilizations. These interactions fueled economic growth, crafted social structures, and influenced technological advancements that shaped human history.17