“
Social hierarchy and leadership in the Neolithic Era played a vital role in shaping early human societies. This blog presents 20 fascinating facts about how communities organized themselves and established governance structures. As agricultural practices developed, social roles became more defined, leading to the emergence of leaders who guided their people through various challenges. These leaders coordinated activities, managed resources, and fostered cooperation among community members. As societies grew more complex, leadership styles evolved to blend authority with collaboration. Understanding these dynamics helps us appreciate how early humans navigated challenges, creating societies that laid the groundwork for future civilizations.1
”
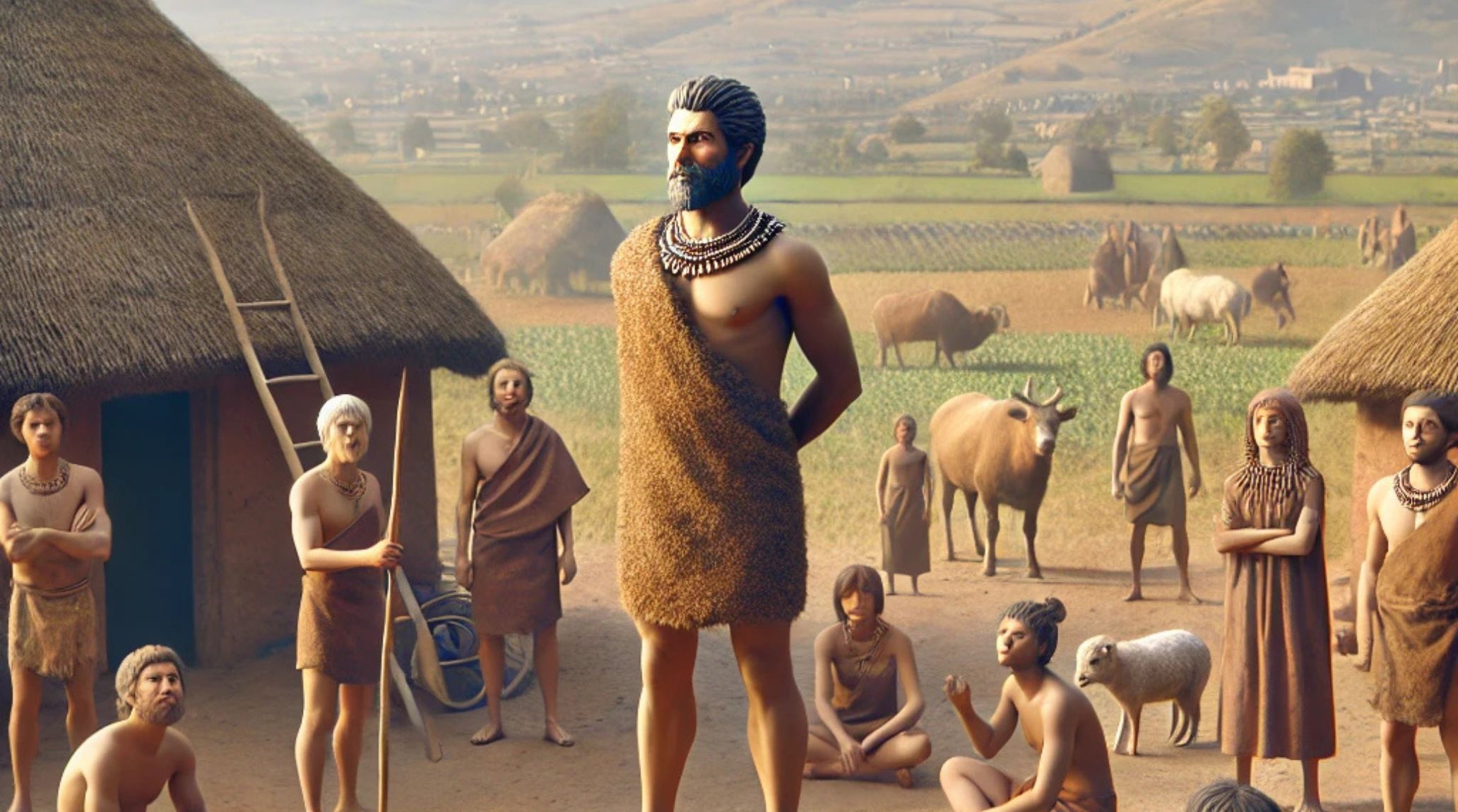
The Neolithic Era transformed social structures, shifting from egalitarian groups to hierarchical societies. Agriculture spurred this change, allowing individuals to accumulate wealth and influence over time.1
As farming flourished, leaders emerged to organize labor and resources. These early rulers showcased the importance of governance in cultivating cooperation and ensuring community survival.2
Archaeological evidence reveals that some Neolithic leaders held dual roles as spiritual figures. They performed rituals to connect their communities with the divine, blending governance and religious authority seamlessly.3
Social stratification arose from resource control. Those who managed fertile land and water sources gained power, shaping community dynamics and influencing leadership decisions based on resource availability.4
Craft specialization contributed to social hierarchy, elevating skilled artisans. As trade expanded, these individuals gained respect and status, illustrating the interdependence between craftsmanship and societal structure.5
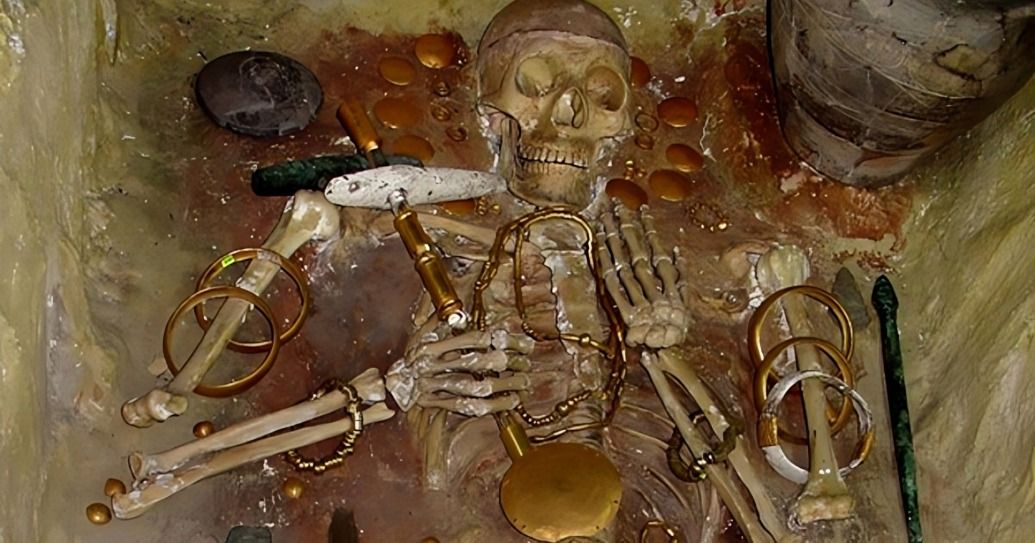

Burial sites show elite Neolithic individuals buried with valuable artifacts, emphasizing social distinction. These grave goods highlighted wealth, prestige, and the significance of influence in leadership roles.
Communal decision-making existed alongside hierarchies, often involving councils of respected elders. This blend of authority and collaboration reflects the nuanced governance of Neolithic communities.6
Sedentism allowed families to establish lineage and status. Ancestral connections began to influence leadership roles, laying the groundwork for future systems based on familial authority.7
Women played crucial roles, with some evidence suggesting they held leadership positions. Their contributions to agriculture and community life indicate a more complex social structure than previously believed.8
Conflict over resources sometimes led to military leadership. Rising competition brought individuals with combat skills to prominence, demonstrating the relationship between leadership, social structure, and environmental challenges.9
Trade relationships shaped social hierarchies, with leaders negotiating alliances. Those excelling in diplomacy gained prestige, highlighting the importance of networking and relationships in establishing power.10
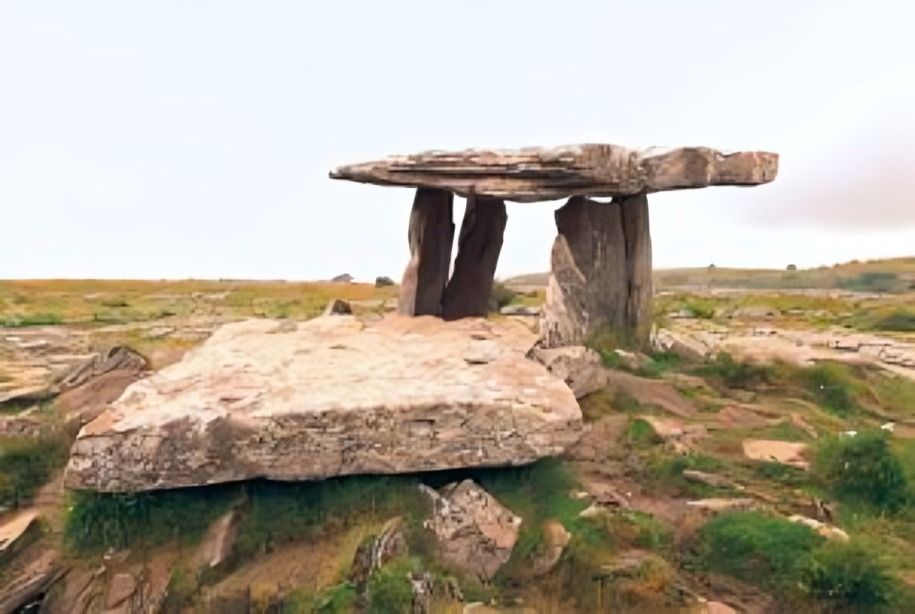

Monumental structures, like megaliths, reflected leadership authority. These impressive constructions served as communal gathering places and symbols of the leaders' influence within their societies.
Rituals reinforced social hierarchy, with leaders playing vital roles. These events solidified status and fostered unity, serving as a means of collective identity and memory.11
As societies grew, organized leadership became essential. Complex agricultural practices required effective management, leading to the development of roles focused on resource distribution and community welfare.12
Leaders often relied on advisors or councils for decisions. This collaborative approach balanced authority with communal input, reflecting the evolving nature of governance and social structures.13
Some leaders served as intermediaries between the divine and their communities. This spiritual aspect elevated their status and reinforced authority, illustrating the blend of religion and governance.14
Social mobility varied, allowing some individuals to rise through achievements or marriages. This opportunity showcased a dynamic social structure that evolved with changing circumstances.15

Neolithic art celebrated leaders, highlighting their societal roles. These depictions conveyed social values and reinforced hierarchies, demonstrating the importance of artistic expression in community identity.
The legacy of Neolithic hierarchies laid the foundation for future civilizations. The governance lessons learned during this era influenced the social structures of subsequent societies throughout history.16
Neolithic leaders thrived on reciprocity. By providing resources and protection, they gained loyalty and support, illustrating that effective leadership relied on mutual benefit and trust.17