“
Throughout medieval Europe, knights embodied the ideals of valor, honor, and service, shaping both military tactics and societal norms. In this exploration, we uncover 20 fascinating facts that illuminate the lives, traditions, and enduring legacy of these noble warriors. From their rigorous training and iconic armor to their role in feudal society and chivalric code, knights represent an enduring symbol of courage and virtue. Join us as we delve into the rich history and cultural impact of knights and chivalry.1
1
”
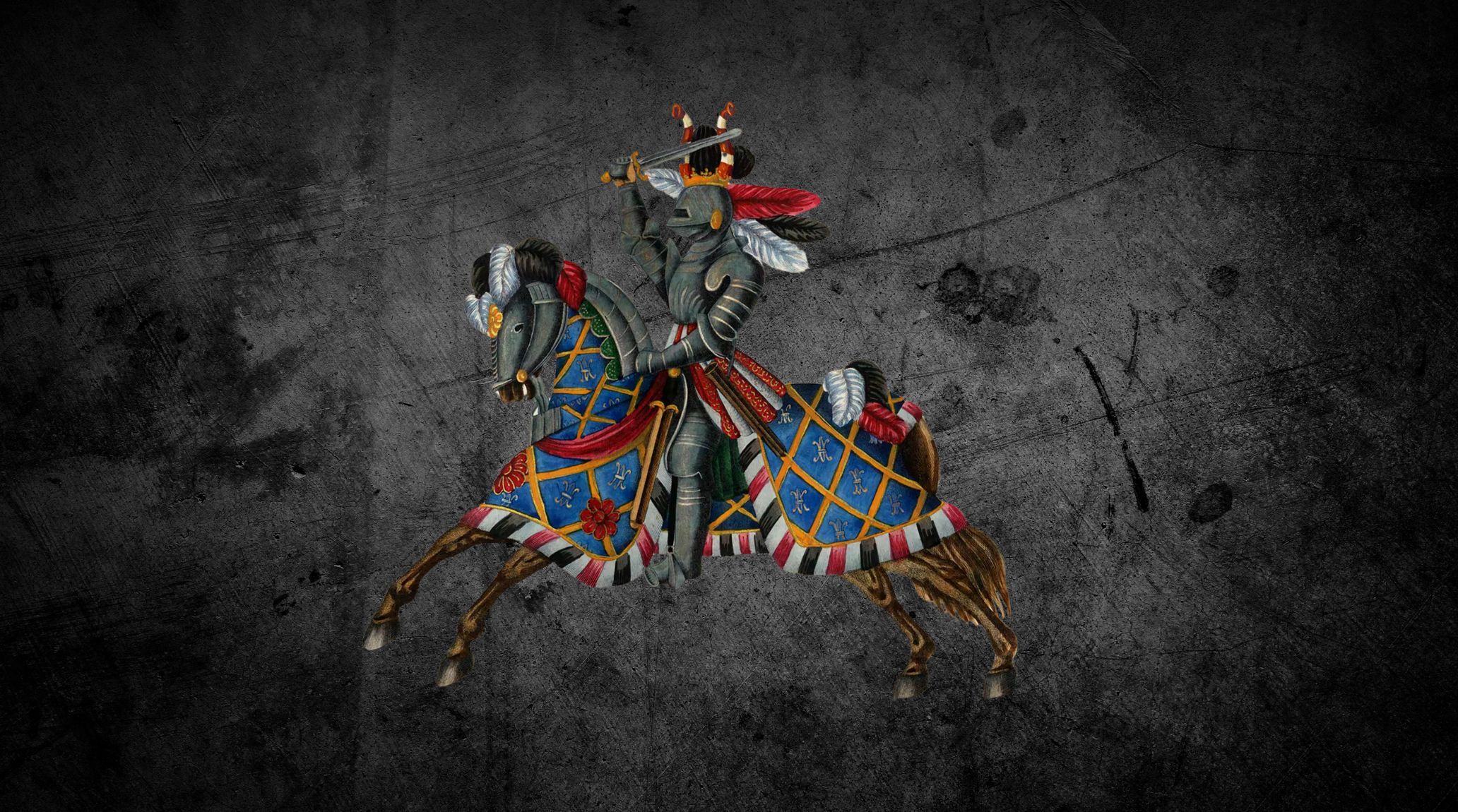
Knighthood emerged in the early Middle Ages as mounted warriors serving feudal lords. Initially, knights were essential in battles and conflicts, and over time, they became symbols of honor and martial prowess in medieval society. 1
The code of chivalry, introduced in the 12th century, outlined virtues like bravery, honesty, and respect for women, guiding knights' conduct on and off the battlefield. This code became a moral and ethical foundation. 2
Knights wore armor made of metal plates and chainmail, wielding swords, lances, and shields designed for maximum protection and efficiency in combat. The development of armor and weaponry was crucial in enhancing their effectiveness. 3
Aspiring knights trained as squires, learning combat skills, horsemanship, and the principles of chivalry under the guidance of experienced knights. This rigorous training prepared them for their future roles and responsibilities as knights. 4

The accolade ceremony marked a squire's transition to knighthood, involving a dubbing ritual where the lord or knight bestowed the title with a tap of the sword on the shoulder.
Tournaments were popular events where knights showcased their prowess in jousting and melee combat. These events attracted spectators, serving as both competitive arenas and social gatherings. 5
Knights played a crucial role in feudal society, serving as military leaders, landowners, and protectors of the realm under their lord's authority. Their responsibilities extended beyond the battlefield to include governance and defense of their lord's lands. 6
Warhorses were bred for strength, agility, and stamina, essential for charging into battle and carrying knights clad in heavy armor. These horses were integral to a knight's effectiveness in combat, requiring specialized care and training. 7
Courtly love was a romantic ideal celebrated by knights, emphasizing admiration, respect, and devotion to noble ladies. This concept served as a source of inspiration and moral refinement, influencing knights' behavior and ideals. 8
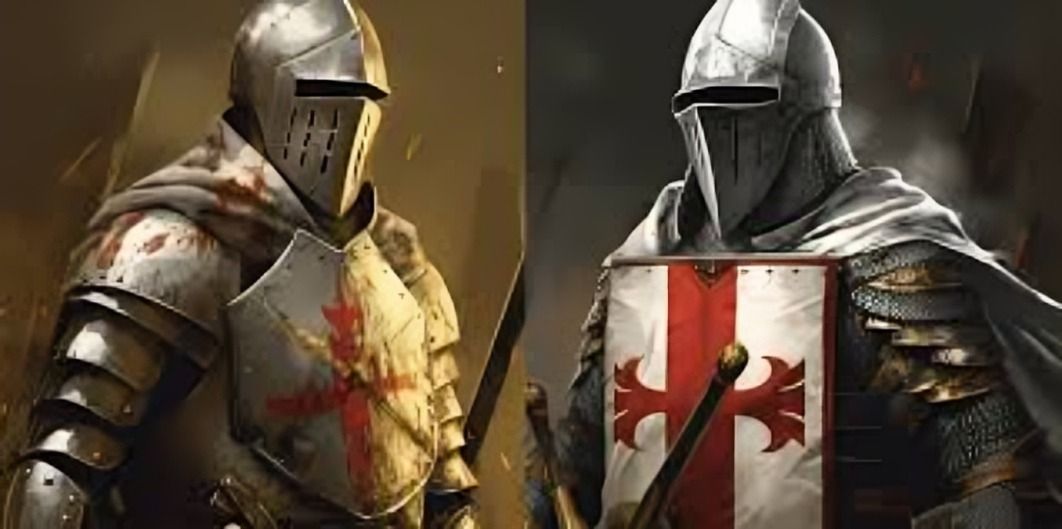

Military orders like the Knights Templar and Hospitallers combined knighthood with religious devotion, defending Christian interests and providing aid to pilgrims. These orders played significant roles in the Crusades and other religious missions.
Knights participated in siege warfare, employing tactics to breach or defend fortified castles and cities during conflicts and Crusades. Their expertise in siege tactics was crucial in the success of military campaigns. 9
Knights engaged in duels to settle disputes or uphold honor, following strict codes of conduct that governed combat and ensured fair play. These duels were not only tests of skill but also mechanisms for resolving conflicts. 10
The decline of knighthood began with changes in warfare tactics, advancements in weaponry, and the rise of centralized monarchies during the late Middle Ages. These factors diminished the traditional role of knights in military and societal contexts. 11
Knights influenced European culture, contributing to art, literature, and societal ideals that shaped perceptions of valor, honor, and loyalty. Their legacy is reflected in numerous works of art and literature from the medieval period. 12
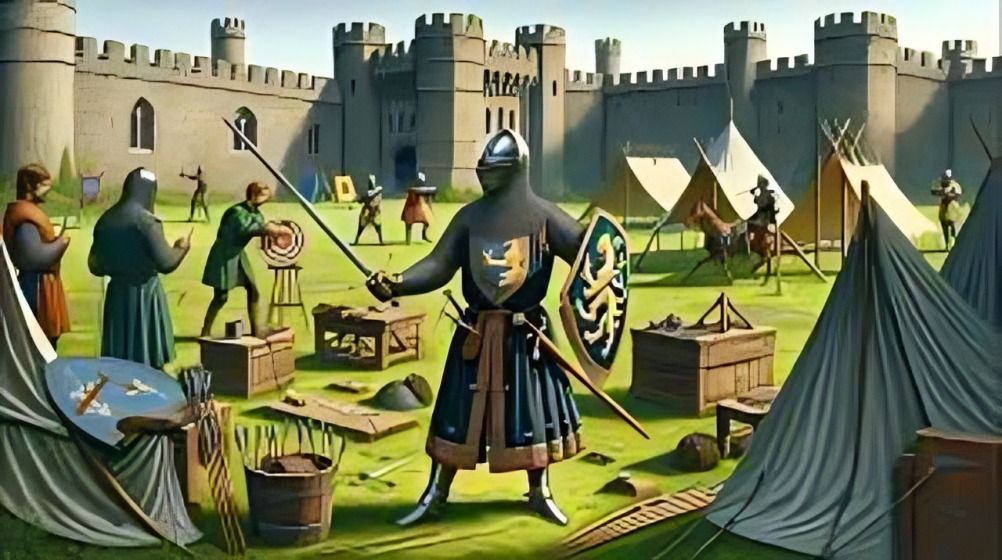

Knights served as mentors to young squires, imparting martial skills, ethical principles, and the responsibilities of knighthood. This mentorship was crucial in maintaining the standards and traditions of knighthood.
Knighthood often required substantial wealth to afford armor and warhorses, reinforcing social distinctions and obligations within feudal society. This financial aspect highlighted the privilege and responsibility associated with being a knight. 13
Knights errant were wandering adventurers who embarked on quests to prove their bravery and uphold chivalric virtues. These adventures often involved overcoming challenges and testing their mettle. 14
Some knights undertook religious pilgrimages to holy sites, seeking spiritual enlightenment, redemption, or divine favor amidst their martial duties. These pilgrimages were an important aspect of a knight's spiritual and personal growth. 15
The legacy of knights and chivalry endures as symbols of courage, honor, and the quest for moral excellence. Their ideals of heroism and justice continue to inspire and resonate across generations. 16
Knights and chivalry inspired epic tales and romances like the Arthurian legends, perpetuating ideals of heroism, questing, and noble deeds. These stories have shaped cultural perceptions of knighthood and continue to captivate audiences today. 17