“
Women in ancient Egypt played multifaceted and pivotal roles that defied conventional expectations of gender dynamics in ancient civilizations. This blog delves into the diverse aspects of their lives, exploring their rights, responsibilities, and enduring influence on one of history's most intriguing civilizations.1
1
”
Women in ancient Egypt enjoyed remarkable legal rights, including the ability to own, inherit, and manage property independently of their husbands. This autonomy was uncommon in many contemporary societies and reflected a society where women had significant economic agency. 1
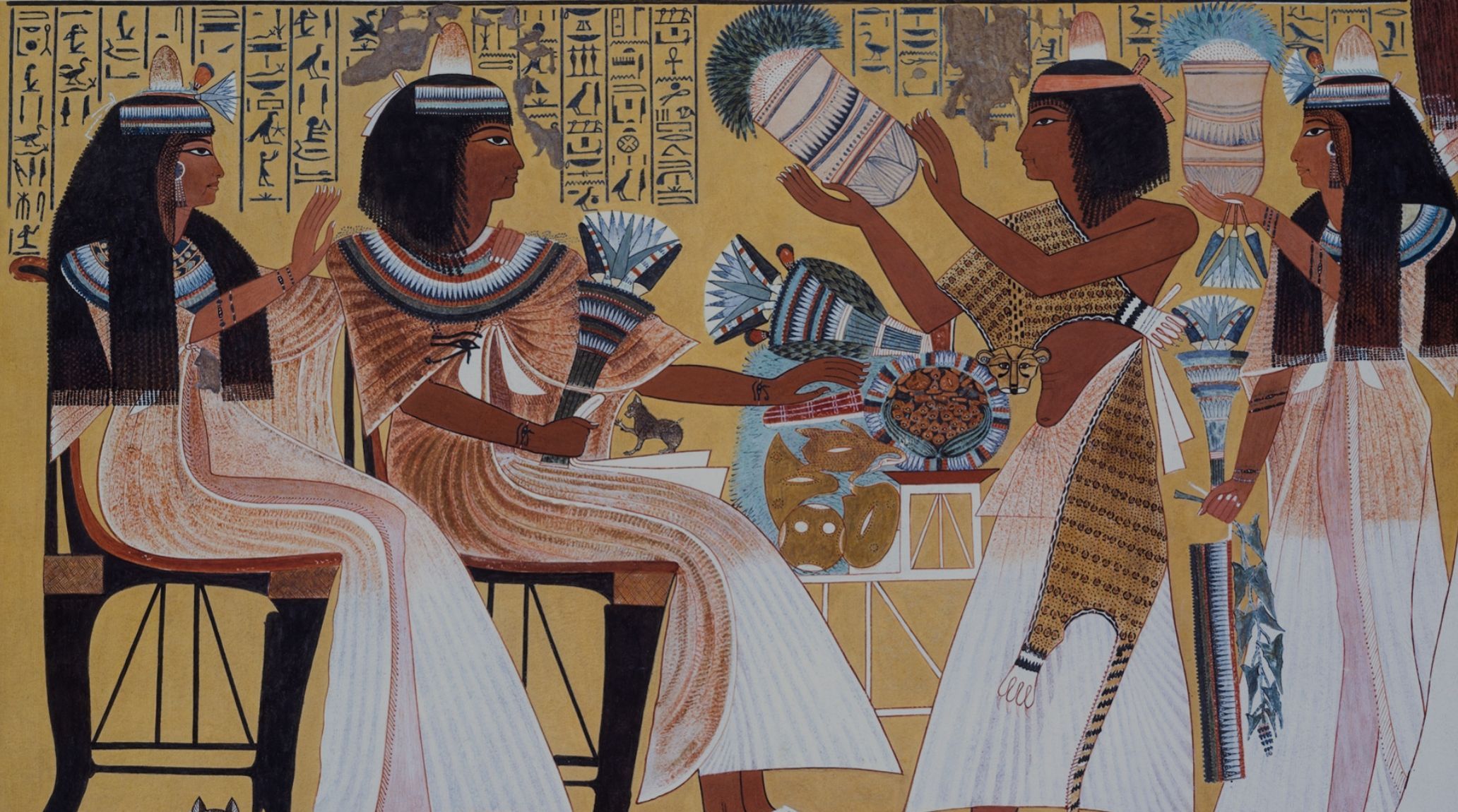
Women were considered equal to men in many respects, although their roles differed, especially in terms of occupation. While men held the primary positions of power both in the household and the nation, women played crucial roles within the home and contributed to the stability of society. 2
Women in ancient Egypt were active participants in the economy as business owners and managers of workshops. Their entrepreneurial spirit contributed to the prosperity and diversity of economic activities in Egyptian society. 3
Serving as priestesses in temples dedicated to various gods and goddesses, women held esteemed positions that allowed them direct access to religious rituals and ceremonies. Their roles were pivotal in maintaining spiritual harmony.4
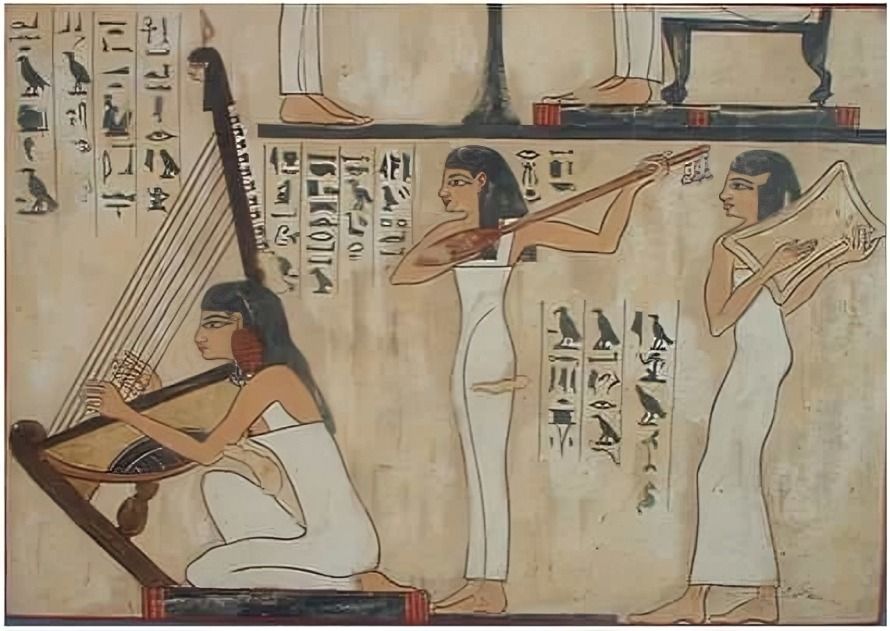

Women contributed to religious ceremonies and communal celebrations as musicians and dancers, using their artistic talents to evoke spiritual and emotional experiences. Their performances were integral to the cultural and religious life of ancient Egypt.
Women of royal lineage wielded considerable influence through titles like "King's Wife" and "King's Mother," which shows their integral roles in royal succession and governance. These titles symbolised both authority and responsibility in the kingdom. 5
A significant number of women in ancient Egypt were literate and proficient in reading and writing hieroglyphs. This literacy empowered them to engage in intellectual pursuits, record their thoughts, and participate in administrative tasks. 6
Women played crucial roles in healthcare as midwives, healers, and even physicians, demonstrating advanced knowledge of medicinal herbs and surgical procedures. Their expertise was vital in ensuring the well-being of their communities. 7
Women in ancient Egypt participated in elaborate burial rituals that honored their status and achievements in life. They were often interred with personal belongings and symbols of their societal roles, ensuring a dignified passage into the afterlife. 8
Nubian women held esteemed positions in Egyptian society, influencing cultural and artistic expressions through their distinctive traditions. Their presence enriched the cultural tapestry of ancient Egypt, evident in art and literature. 9
The Harem Conspiracy involving royal women against Ramesses III highlights complex power dynamics within the royal court. This historical intrigue underscores the political acumen and influence wielded by women in the highest echelons of Egyptian society. 10
Clothing and jewellery served as visible markers of a woman's social status and role in ancient Egyptian society. These attire choices not only expressed personal identity but also conveyed cultural norms and affiliations within the community. 11
Women had legal rights to inherit property from their fathers in the absence of male heirs, ensuring their financial independence and continuity of family wealth. This inheritance law affirmed their status as rightful heirs in the familial and societal hierarchy. 12
Devotion to the goddess Isis provided women with spiritual guidance and solace, emphasizing her role as a nurturing and protective deity. The cult of Isis offered avenues for personal piety and communal worship, fostering spiritual fulfillment. 13
Women practiced diverse forms of magic aimed at protection, healing, and fertility, drawing on ancient Egyptian beliefs in supernatural forces. Their expertise in magical rituals contributed to communal well-being and individual prosperity.
In Ancient Egypt, social dignity was not based on gender but rather on social status. This means that both men and women could attain respect and influence according to their roles and achievements within society. 14
The most prestigious position a woman could hold in Ancient Egypt, starting from the Middle Kingdom (2040-1782 BCE), was that of the God's Wife of Amun. While there were several "God's Wives" associated with various deities, during the Middle Kingdom.15
Artistic representations frequently depicted women nursing children, symbolizing their roles as nurturers and custodians of familial continuity. These maternal images conveyed ideals of care and affection within ancient Egyptian society. 16
Women's study of celestial movements and their impact on daily life demonstrated advanced knowledge of astronomy and astrology. Their interpretations of cosmic events influenced societal decisions and personal destinies, shaping cultural practices.17
Engaging in shamanic healing rituals, women utilized herbs and incantations to alleviate ailments and promote spiritual well-being. Their holistic approach to healthcare integrated physical and metaphysical dimensions, fostering community health. 18