“
Water is crucial in energy production across various sectors, from hydropower and thermal power plants to bioenergy and geothermal systems. Water's Role in Energy Production is integral to converting natural energy sources into electricity and ensuring efficient operations. Understanding water's multifaceted role highlights its importance in sustainable energy practices and emphasizes the need for careful management to balance energy production with environmental stewardship.1
1
”
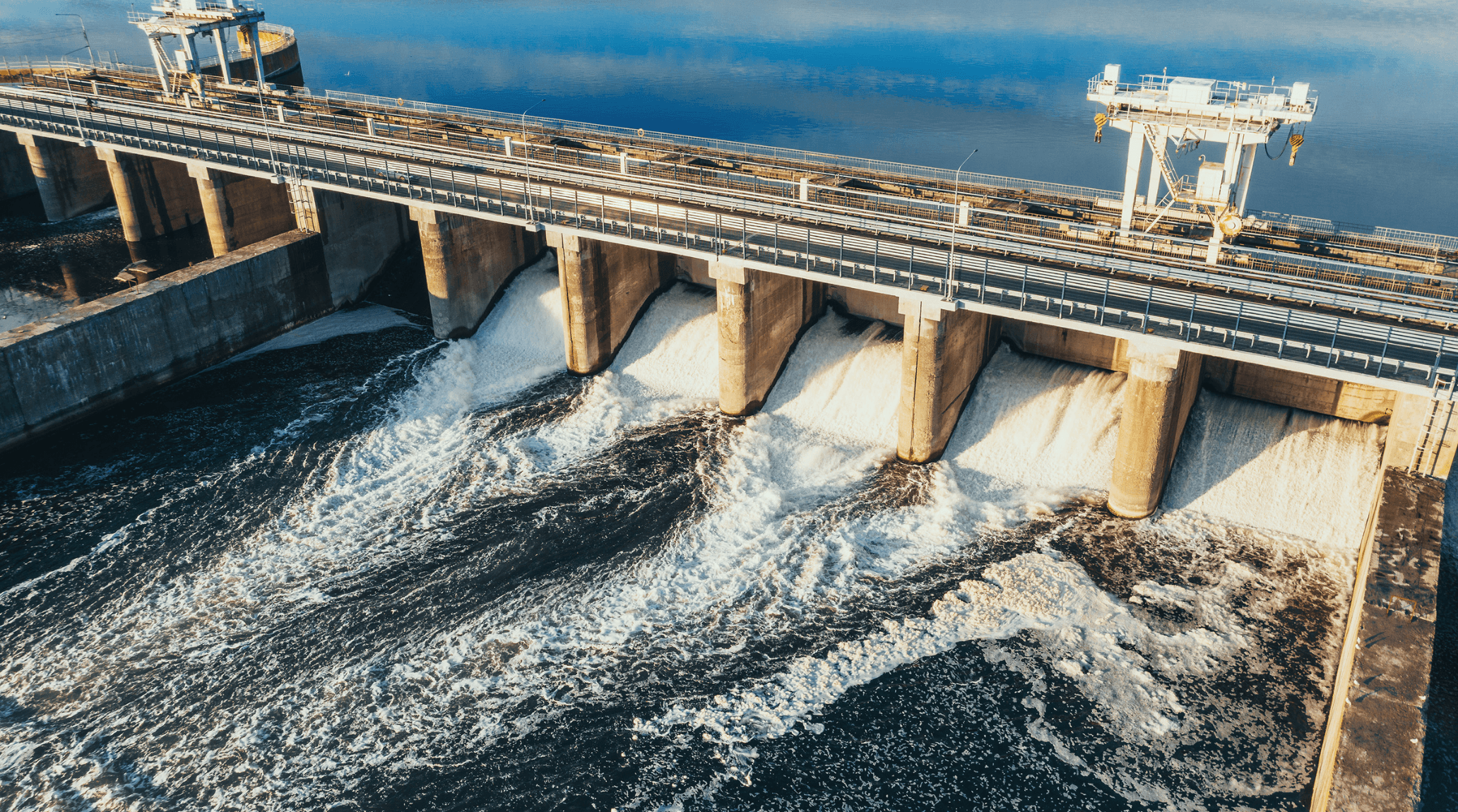
Water is a primary driver in hydropower, where flowing water spins turbines to generate electricity. This renewable energy source accounts for about 16% of global electricity production, harnessing the kinetic energy of rivers and dams. 1
In thermal power plants, water is essential for cooling machinery to prevent overheating and maintain operational efficiency. This role is vital for the continuous and reliable production of electricity in such facilities. 2
Wave energy captures the movement of ocean waves to generate electricity. Special devices called wave energy converters harness the kinetic energy of waves, converting it into usable power and offering a promising renewable energy source. 3
Algae, which thrive in aquatic environments, are used to produce biofuels. These algae-based fuels provide a renewable and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, offering an eco-friendly option for energy production and reducing our reliance on non-renewable resources. 4
Water is crucial in biomass cultivation, used in bioenergy production through processes like fermentation, gasification, and combustion. Its role is integral to bioenergy, supporting the development of renewable energy sources. 5
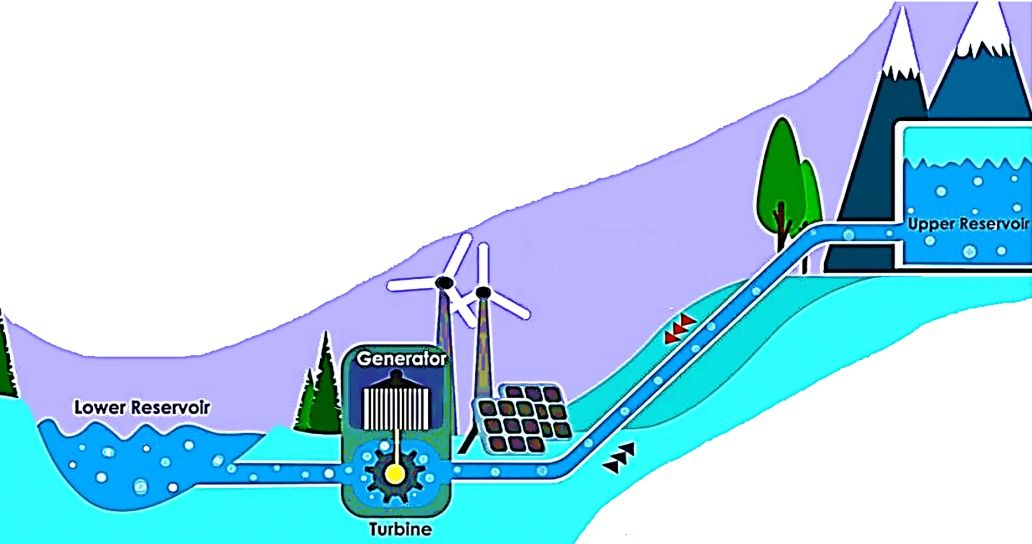
In pumped-storage hydroelectricity, water is pumped to a higher elevation during periods of low demand and released to generate electricity during peak demand. This process underscores water's importance in balancing energy supply and demand.
In arid regions where freshwater resources are scarce, desalinated water is often necessary for cooling in power generation. This highlights the critical role of desalinated water in maintaining efficient energy production in such areas. 6
Water is essential for hydrogen production through electrolysis, where electricity splits water into hydrogen and oxygen. This process contributes significantly to clean energy technologies and supports the development of a sustainable energy future. 7
Geothermal power plants use water to extract heat from the Earth's core, which is then converted into electricity. This showcases water's crucial role in harnessing geothermal energy and generating sustainable power. 8
Water is used in oil and gas extraction, including hydraulic fracturing (fracking) and enhanced oil recovery (EOR). This demonstrates its significance in fossil fuel production and highlights the broader impact of water on energy resources. 9
Tidal energy harnesses the gravitational pull of the moon and sun on Earth's oceans to generate power. Tidal stream generators and tidal range power plants capture the kinetic and potential energy from tidal movements. 10
Desalination plants use energy to remove salt from seawater, making it suitable for use in energy production. This process supports energy plants by providing freshwater for cooling and other operational needs. 11
Water withdrawal for energy production can impact aquatic ecosystems, making it crucial to manage and regulate water use carefully. This ensures minimal environmental impact and promotes the sustainability of energy production practices. 12
Some innovative power systems combine water with hydroponics to grow plants while generating energy. These systems use water for both plant cultivation and to drive small-scale hydroelectric generators. 13
Water is essential for growing biomass used in bioenergy production. Plants like corn and sugarcane, which are converted into biofuels, rely on water for their growth, highlighting its role in sustainable energy solutions. 14
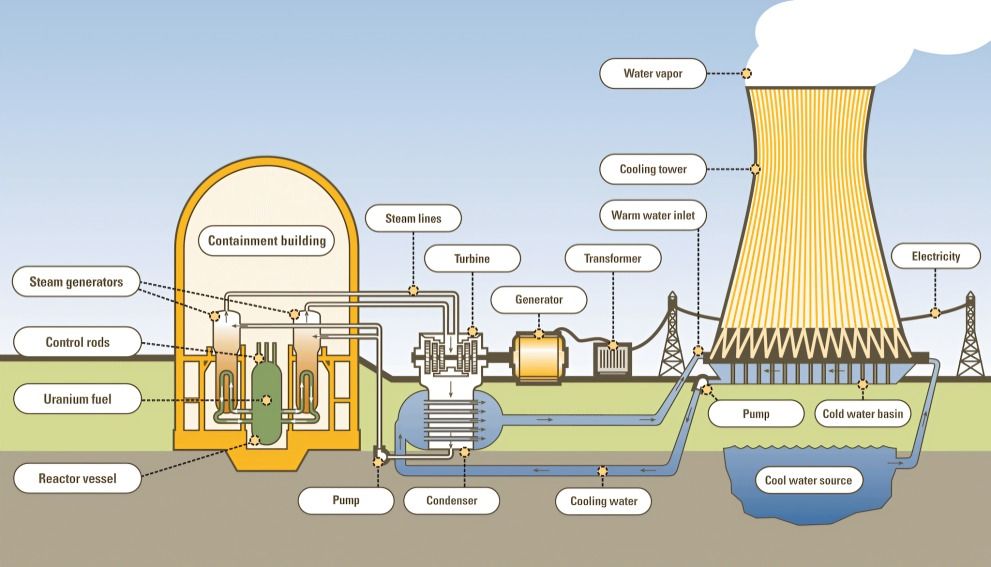
In nuclear power plants, water acts as a coolant and neutron moderator, essential for maintaining nuclear reactions and transferring heat to generate steam. This is critical for the efficient production of electricity in nuclear facilities.
Different energy sources have varying water footprints, with bioenergy and fossil fuels generally requiring more water compared to renewable sources like wind and solar photovoltaic systems. This emphasizes the need for water-efficient energy solutions. 15
Hydropower provides essential electricity to developing countries, supporting economic growth and improving living standards. Small-scale hydroelectric projects can offer affordable and sustainable energy solutions in remote areas. 16
Water is used in cooling systems for wind turbine generators. Efficient cooling helps maintain optimal performance and extends the lifespan of wind turbines, which are integral to renewable energy infrastructure. 17
Government policies often regulate water use in energy production to ensure sustainable resource management and minimize environmental impacts. This reflects the critical role of policy oversight in balancing water and energy needs for future sustainability. 18


