“
Ancient Rome was not only a civilization known for its architectural marvels and military prowess but also for its ground breaking innovations in science and technology. This article highlights 20 remarkable Roman innovations that transformed science and technology.1
1
”
The Romans developed a durable form of concrete using volcanic ash, lime, and seawater, which allowed their structures to withstand the test of time. This innovation enabled the construction of massive and enduring buildings like the Pantheon. 1
The Romans built an extensive network of roads that spanned over 250,000 miles. Their use of layered construction and roadbeds helped roads last longer and facilitated efficient travel and trade across the empire.2
Introduced by Julius Caesar in 45 BCE, the Julian Calendar reformed the Roman calendar system by creating a year of 365.25 days, improving the accuracy of timekeeping and aligning the calendar with the solar year. 3
The Romans invented the hypocaust system, an early form of central heating. This system circulated hot air beneath floors and within walls to heat buildings, including baths and private homes. 4
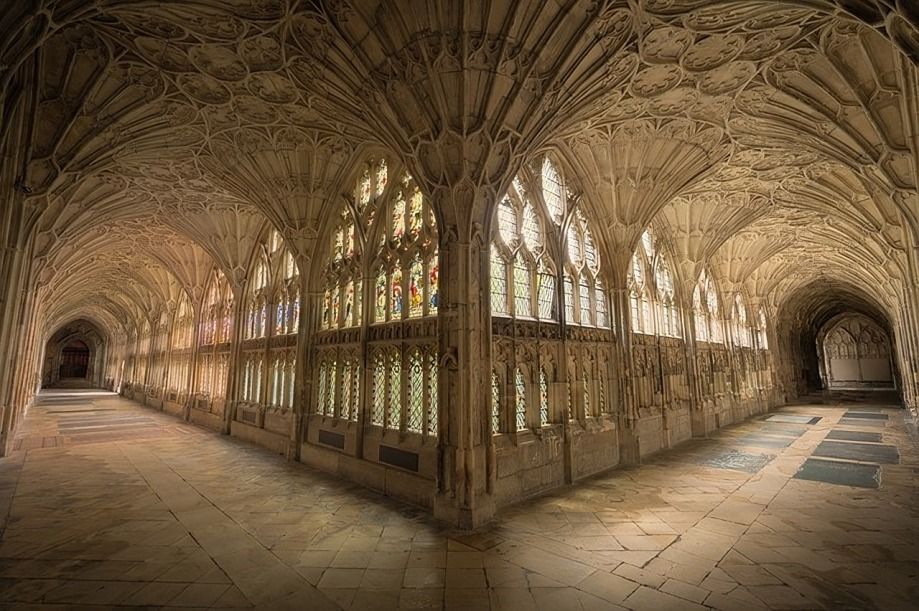

The Romans perfected the use of arches and vaults in their architecture. These structural elements allowed them to build larger and more stable structures, such as the Colosseum, which could support vast crowds.
Introduced by Julius Caesar in 45 BCE, the Julian Calendar reformed the Roman calendar system by creating a year of 365.25 days, improving the accuracy of timekeeping and aligning the calendar with the solar year. 5
The Romans invented the hypocaust system, an early form of central heating. This system circulated hot air beneath floors and within walls to heat buildings, including baths and private homes. 6
The Romans were the first to give daily news to their citizens through handwritten announcements displayed publicly in Rome. These updates included political news, military events, and major scandals. 7
Roman engineers built durable and functional bridges using concrete, stone, and brick. The Pont du Gard in France and the Pons Fabricius in Rome are notable examples of their advanced bridge-building techniques. 8
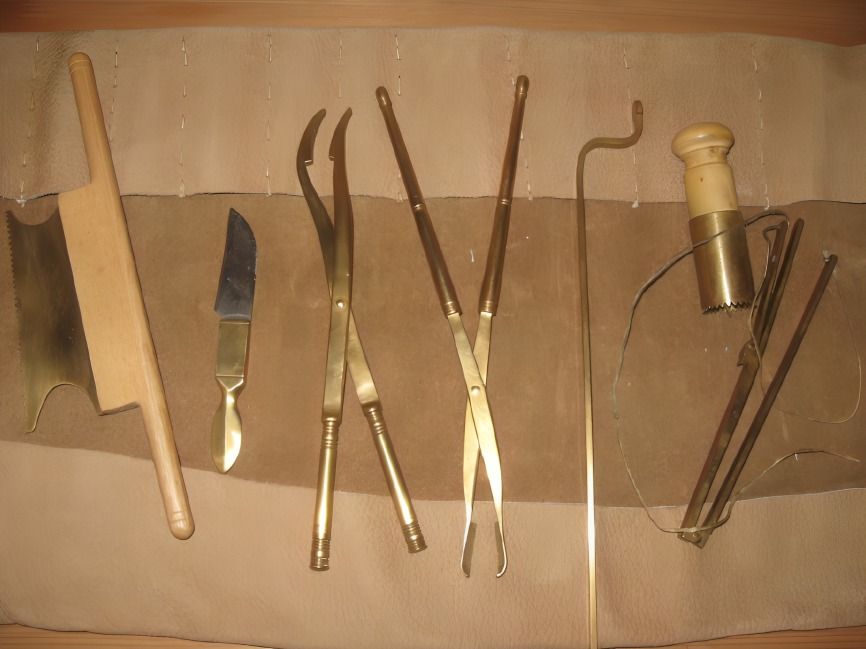
Roman medical practitioners used a range of advanced surgical tools, including forceps, scalpels, and catheters. Their use of these tools laid the groundwork for modern surgical practices.
To build harbors and piers, Romans invented a type of hydraulic cement that was set underwater. This allowed them to construct impressive maritime structures like the Portus harbor in Rome. 9
The Roman calendar included unique months and the institution of leap years. This calendar system influenced the development of the Gregorian calendar, which is still in use today. 10
The Romans pioneered the design of country estates known as villas, which included advanced features such as gardens, heating systems, and decorative mosaics, influencing future European architectural styles. 11
Although controversial, the organization of gladiatorial games demonstrated Roman innovation in entertainment and crowd control. They used elaborate arenas and sophisticated logistics to manage these large-scale events. 12
The Twelve Tables were one of the earliest codifications of Roman law. This legal code provided a framework for legal procedures and rights that influenced modern legal systems. 13
The Romans utilized water mills to grind grain into flour, marking an early use of hydropower for industrial purposes. These mills significantly increased the efficiency of grain processing. 14
The Roman numeral system was a sophisticated method of counting and record-keeping that used combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet. It influenced the development of numerical systems in Europe. 15
The Roman Forum was an innovative space for political, economic, and social activities. It served as the heart of public life in Rome, featuring temples, basilicas, and marketplaces. 16
The Romans developed a state-run postal system known as the cursus publicus. It used a network of relay stations and mounted couriers to deliver messages across the empire efficiently. 17
Roman urban planning included the grid layout for cities, with streets intersecting at right angles. This design facilitated organized growth and efficient movement within densely populated urban areas.18