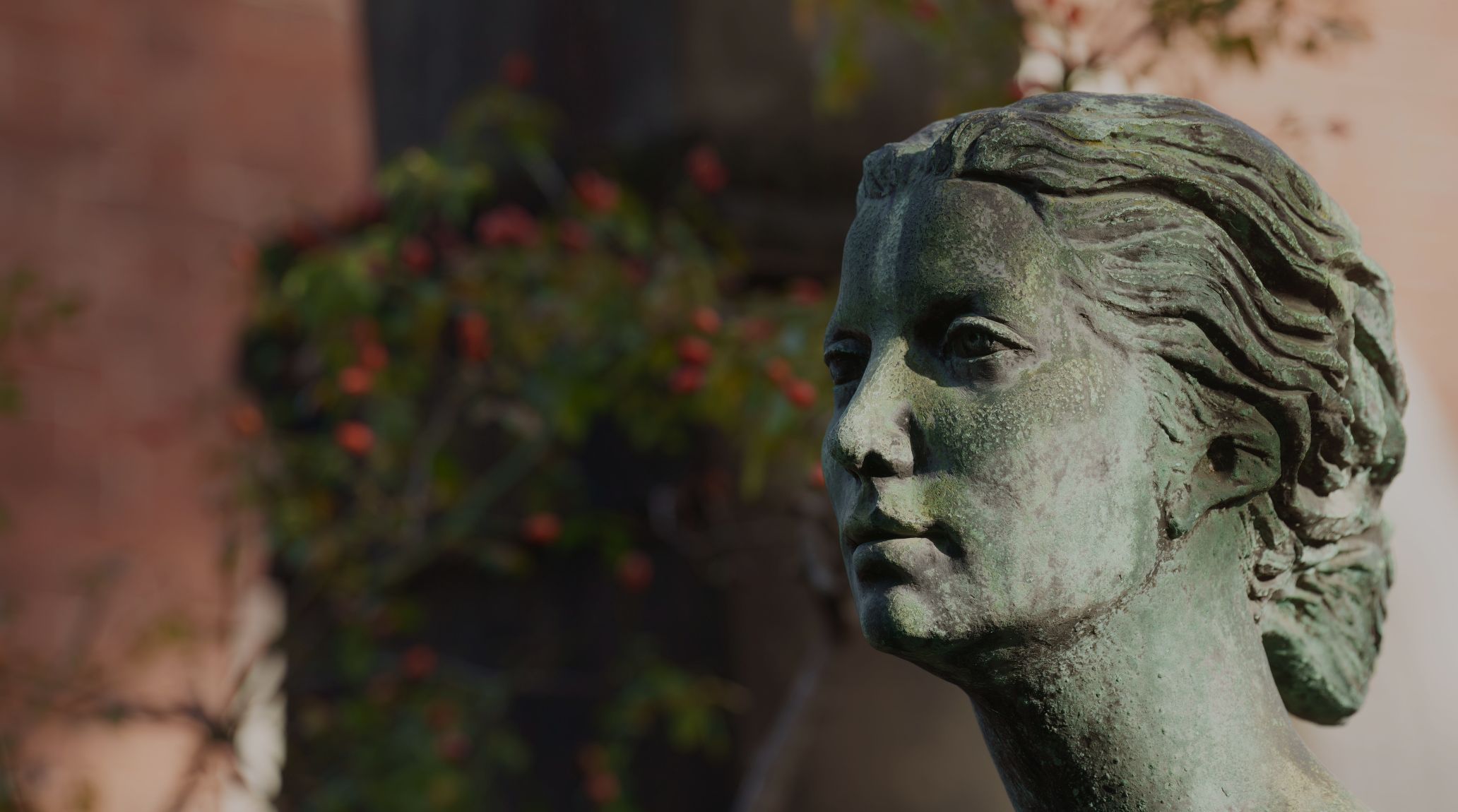“
Roman art and literature not only adorned public spaces and private homes but also conveyed deep insights into Roman life, values, and beliefs. This article explores 20 captivating facts about Roman art and literature, shedding light on how these artistic and literary forms shaped and reflected the culture of ancient Rome.1
1
”
Roman culture, influenced initially by the Greeks, evolved uniquely as the empire expanded, evident in their art, literature, and architecture. Notable examples include the Colosseum, where public games were held. 1
Roman art during the Republic was known for veristic portraiture, which emphasized realistic, often unflattering details to capture the true appearance of individuals. This style was intended to convey the virtues of age and experience. 2
Poetry was the most renowned form of Roman literature, with notable poets like Horace, Ovid, Lucan, and Virgil, who penned influential works such as The Aeneid, Rome's national epic. 3
Cicero was a major figure in Roman literature and oratory, known for his philosophical writings and speeches. His works emphasized rhetoric and the art of persuasion, influencing later Western literature and political thought.4
Romans developed an interest in philosophy following their conquest of the Greeks, with Cicero emerging as a prominent philosopher. He encouraged skepticism by urging people to question ideas and facts. 5
Sports and circuses were used by emperors to keep the populace entertained. These circuses featured games, including gladiatorial combat and battles involving animals, enslaved individuals, and prisoners. 6
Venues like the Colosseum hosted grand chariot races and various other tournaments, which were major forms of entertainment in ancient Rome. The Colosseum, completed in 80 AD, could hold up to 50,000 spectators.7

Roman art is famous for its bronze and marble sculptures, murals, frescoes, portraiture, and vase-painting, as well as its architectural marvels like amphitheaters and domes.
Roman art is distinguished by its early use of verism for hyper-realistic representations, which later shifted to idealism during Imperial Rome to glorify rulers. Unlike Greek art's focus on beauty and philosophy, Roman art, including frescoes. 8
Roman art spanned various mediums, including coin art, fine jewelry, and metalwork, showcasing a diverse range of creative expressions. Sculpture and perspective art, heavily influenced by Greek styles, were frequently replicated. 9
Wealthy Romans often personalized their environments by incorporating images of themselves or their ancestors into their art. This practice not only reflected their status and heritage but also reinforced familial and social connections. 10
Romans predominantly created historical sculptures in relief, unlike the Greek tradition of free-standing sculptures. Small sculptures were viewed as luxury items, while molded relief decorations on pottery. 11
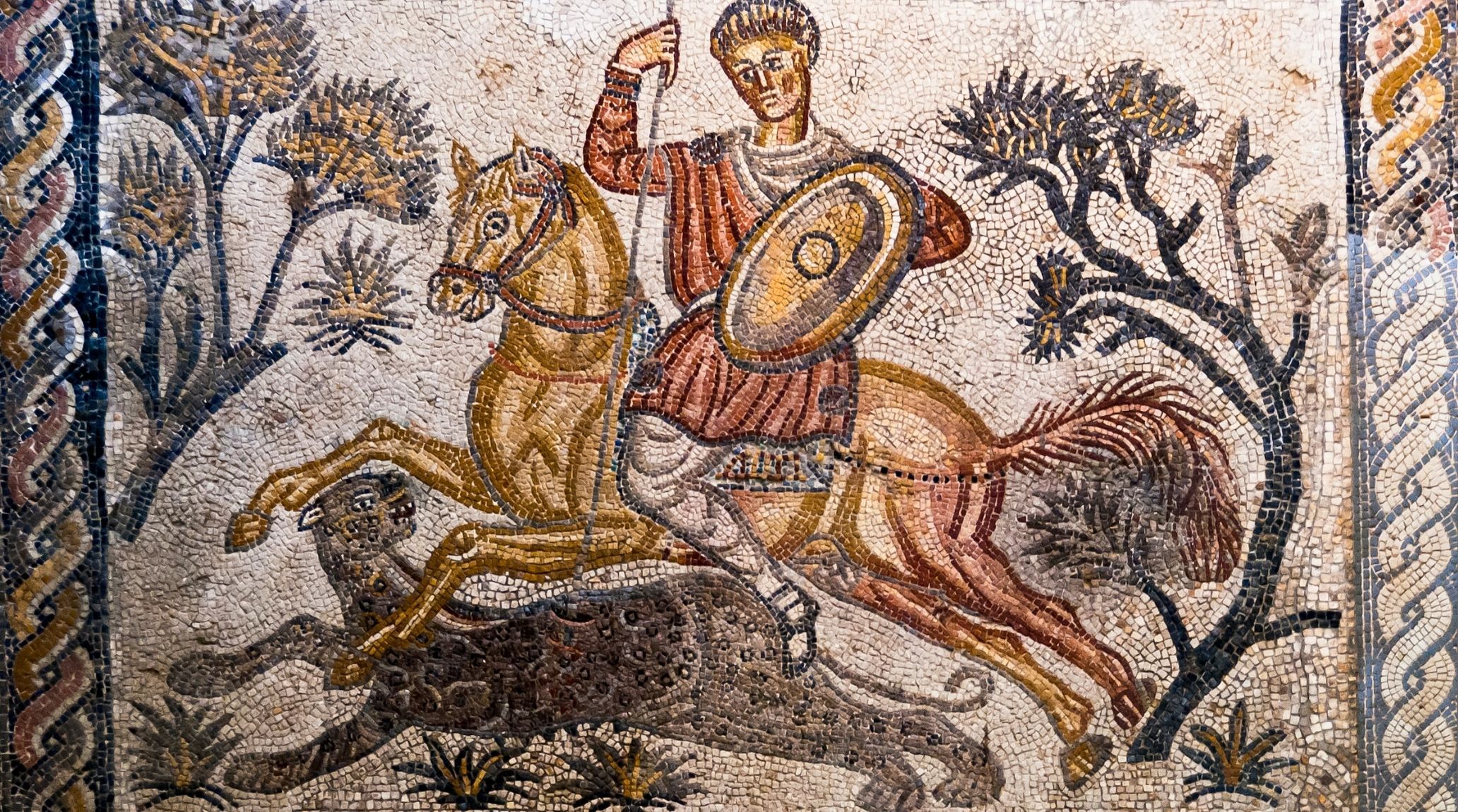
The most famous surviving examples of Roman painting are the wall paintings from Pompeii and Herculaneum, preserved by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 CE. These artworks offer invaluable insights into Roman life and aesthetics. 12
Veristic portraiture, characterized by highly realistic and detailed depictions, was a hallmark of Roman art during the Republic. However, its prevalence declined in the 1st century BCE as civil wars and the rise of powerful individuals began. 13
Many Fayum mummy portraits exist from Roman Egypt. These are painted wooden busts attached to the outside of mummies by the Romanized middle class. While they have local features, they also show the broader Roman style of portrait painting. 14
Roman painting encompassed a wide range of subjects, including landscapes and narrative themes from literature and mythology. It primarily took the form of frescoes. The main colors used in Roman paintings were deep red, yellow, green, and black. 15
The Romans treated art as a commodity, using it to glorify their rulers and reinforce socio-political power. Additionally, Roman art was heavily influenced by Classical Greek art. 16
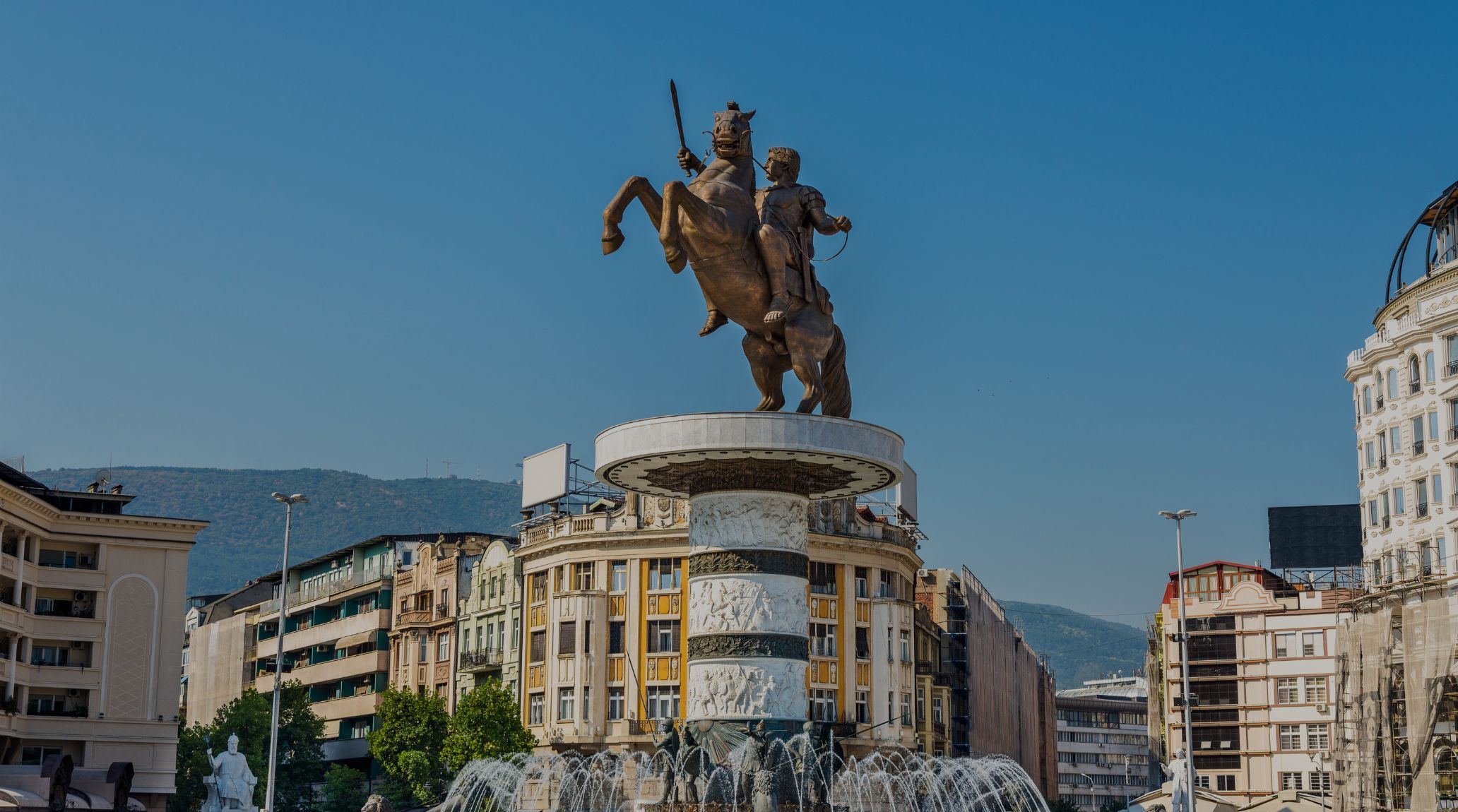
Two notable examples of Roman art are sculpture and mosaic. The Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius is a famous Roman sculpture, while the Alexander Mosaic is a renowned example of Roman mosaic art. 17
Roman glassware was highly prized for its craftsmanship and innovation. Techniques such as blowing and molding allowed for the creation of intricate and delicate glass vessels. 18
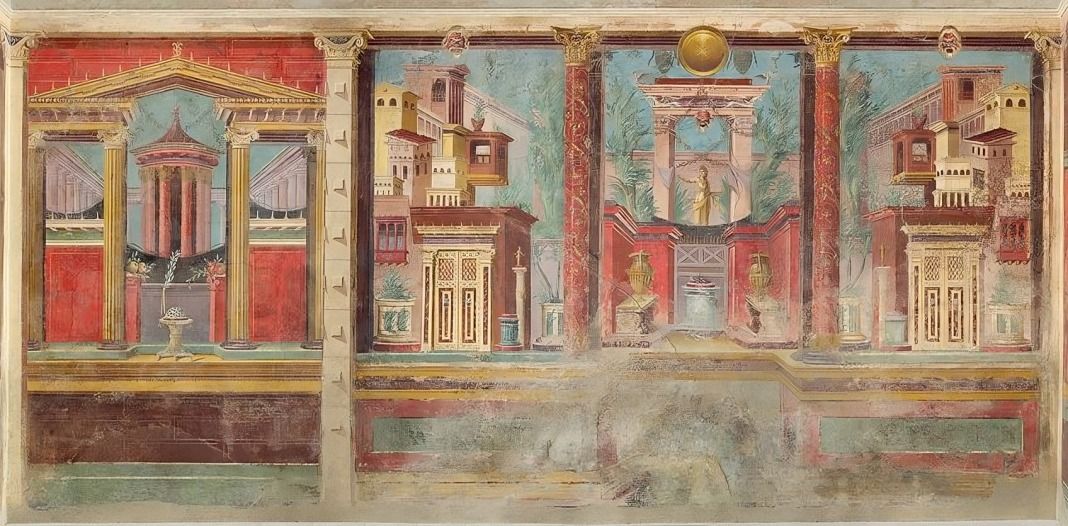

Roman paintings were primarily executed as murals and frescoes. Murals were painted directly onto walls, while frescoes involved applying water-based pigments onto wet plaster, allowing the colors to bond with the plaster as it dried, creating a lasting image.