“
The Paleolithic Era, also called the Old Stone Age, is a significant period in human history. It marks when our ancestors started using stone tools and shaping their environment. This blog presents 20 Interesting Facts About the Paleolithic Era, exploring how early humans survived, created art, and developed primitive technologies. 1
1
1
1
”
Homo habilis, an early human species, emerged during the Paleolithic Era. Known as "handymen," they were the first to create and use stone tools for cutting and hunting, signalling a major shift in human technological evolution.1
The Paleolithic Period is divided into Lower, Middle, and Upper stages, but anthropologists avoid strict timelines as technologies and tools emerged at different times across regions, making it difficult to define precise boundaries for each phase.2
Humans first controlled fire during the Paleolithic Era, a major milestone in history. It provided warmth, protection, and a way to cook food, leading to better nutrition and allowing humans to thrive in various environments.3
Paleolithic humans were nomadic, moving from place to place in search of food and resources. They primarily relied on hunting, fishing, and gathering wild plants, as agriculture had not yet been developed.4

Cave paintings from the Paleolithic period, such as those found in Lascaux, France, are some of the oldest known examples of human art. These intricate depictions of animals and symbols reveal the early humans' creativity and cultural expression.
The earliest known burials of human remains occurred during the Paleolithic Era, suggesting that early humans may have developed spiritual beliefs or rituals regarding death, laying the foundation for later religious and cultural practices.5
During the Paleolithic Era, human diets were diverse, featuring meat from large animals, fish, fruits, nuts, and seeds. This nutrient-rich, hunter-gatherer diet has inspired modern eating trends, including the popular Paleo diet.6
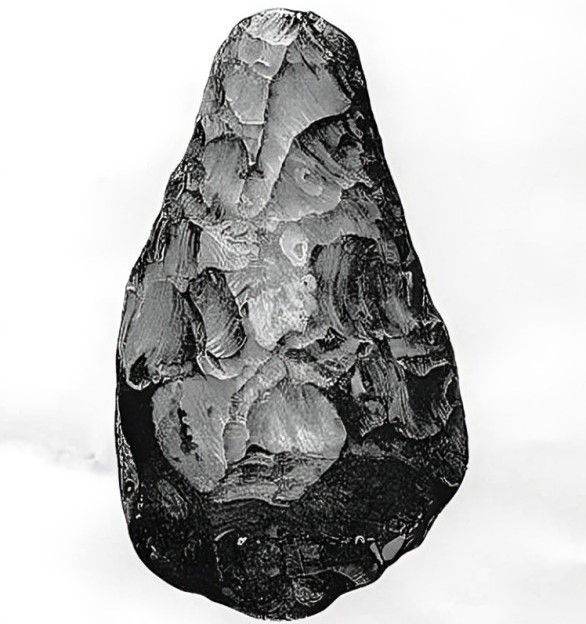

The invention of the hand axe during the Paleolithic Era was revolutionary. It was used for multiple purposes, including cutting meat, skinning animals, and chopping wood, representing the versatility and ingenuity of early tool-making.
The Paleolithic Era witnessed the first human migrations out of Africa. Early humans began exploring new territories, eventually spreading to Europe, Asia, and beyond, leading to today's global population distribution.7
The invention of clothing likely occurred during the Paleolithic Era, as early humans adapted to colder climates by fashioning garments from animal skins, offering them protection against the harsh environments they encountered.8
Language likely began in the Paleolithic Era, though no direct evidence exists. Communication was crucial for hunting coordination, social organization, and passing down knowledge.9
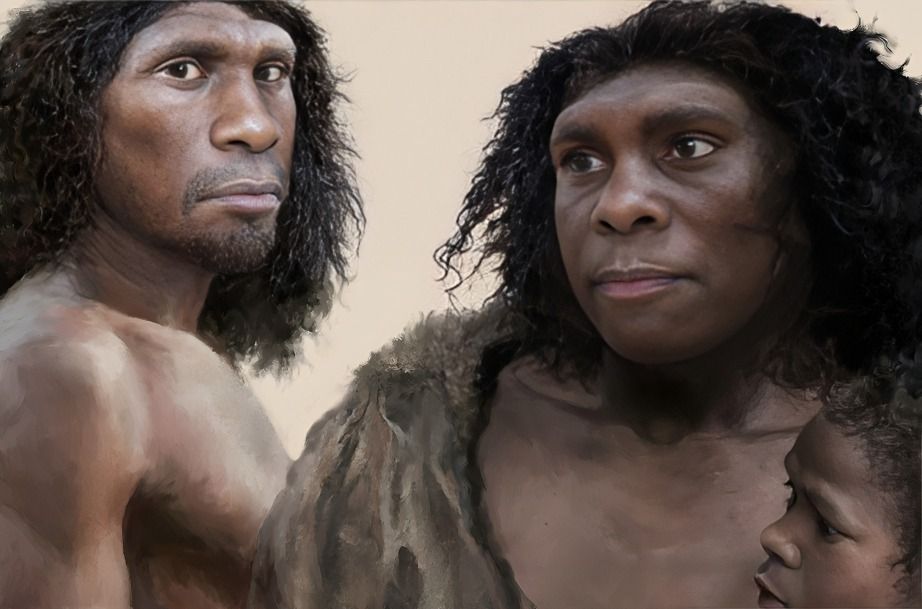

Neanderthals, a close relative of modern humans, lived during the later stages of the Paleolithic Era. They were skilled hunters, used fire, and even had some form of language, making them a sophisticated species before their eventual extinction.
The Paleolithic Era saw the creation of the first personal ornaments, such as necklaces made from shells and bones. These early forms of adornment suggest that humans had a sense of identity and possibly social hierarchies.10
Early humans of the Paleolithic Era utilized natural shelters, like caves and rock overhangs, for protection. These provided shelter from the elements and predators, offering them security as they navigated their challenging environment.11
During the Pleistocene, the mammoth steppe was home to giant mammals, including woolly mammoths, woolly rhinoceroses, and cave lions. These massive creatures thrived in the cold, vast plains and adapted to the harsh environments of the Ice Age.12
Paleolithic humans developed primitive weapons like spears and clubs for hunting large game, such as mammoths and bison. These innovations allowed them to become highly effective hunters, contributing to their survival and success in the wild.13
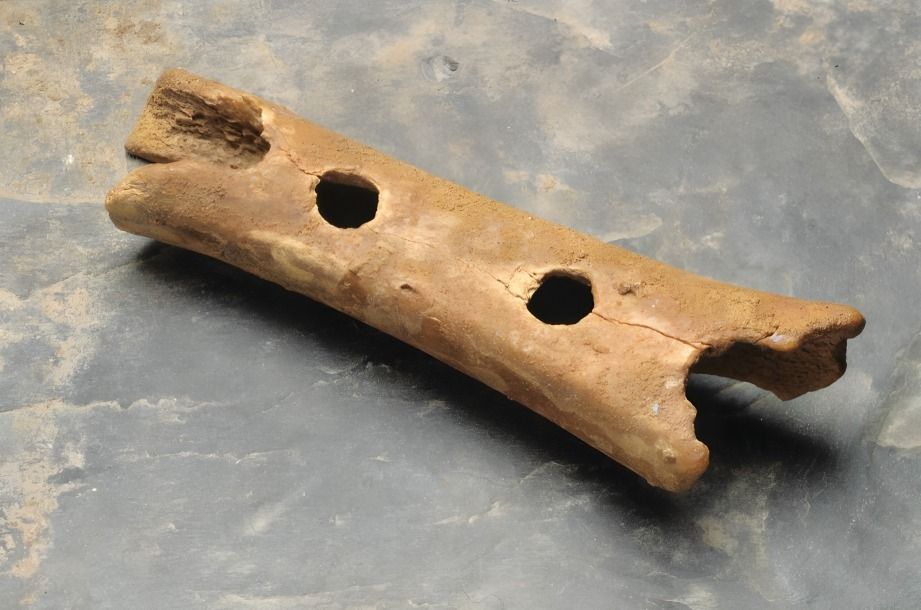

One of the earliest known musical instruments, a flute made from a vulture bone, was discovered in the Paleolithic Era. This suggests that music played a role in social or ritual activities, reflecting the creative nature of early humans.
Artistic expression flourished during the Paleolithic Era, with early humans creating carvings, figurines, and intricate cave paintings. These artistic endeavours indicate that early humans profoundly appreciated beauty and storytelling.14
Stone tool use in the Paleolithic Era is divided into three stages: Lower, Middle, and Upper Paleolithic. Each period marked advancements in tool-making, showcasing early humans' growing intelligence, adaptability, and survival skills.15
Anthropologists suggest the Paleolithic Era had gender roles, with men hunting large game and women gathering plants and small animals, though these roles likely varied among different groups.16