“
Paleolithic Artifacts and Archaeology offer a fascinating glimpse into the lives of our ancient ancestors, revealing their creativity, adaptability, and incredible ingenuity. This blog will explore 20 intriguing facts about Paleolithic artifacts, highlighting their immense significance in understanding human evolution and the cultural developments that laid the foundation for future civilizations. 1
1
1
”
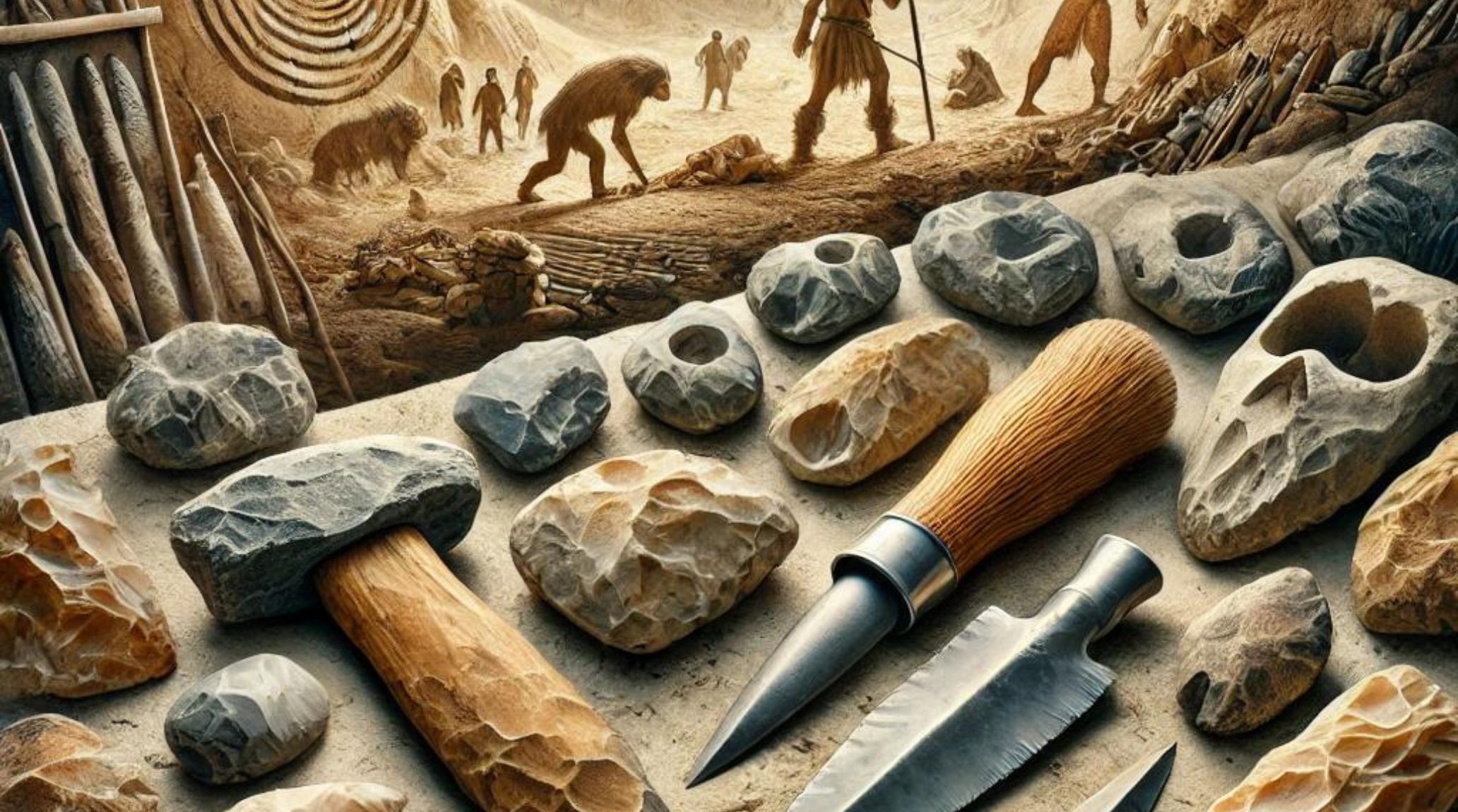
Paleolithic artifacts, mostly found in caves, offer a remarkable insight into early human existence, showcasing their tool-making abilities and artistic expression dating back over 40,000 years.1

The Lascaux Cave paintings in France, with over 600 meticulously depicted animals, highlight early humans' connection to nature and their profound understanding of the surrounding environment.
Discovered in 1994, the Chauvet Cave paintings feature breathtaking depictions of lions, horses, and rhinoceroses, dating back around 36,000 years, showcasing ancient artistic creativity.2
The Venus of Willendorf, a 25,000-year-old statuette found in Austria, exemplifies prehistoric art, representing fertility symbols and highlighting the significant role of women in early societies.3
Stone tools from Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania, dating back around 1.8 million years, reveal the sophistication of early hominins and provide valuable insights into their daily survival skills.4
Engraved ochre found in the Blombos Cave in South Africa, dating back 75,000 years, demonstrates early humans' capacity for symbolic thought and artistic expression through detailed carvings.5
Ochre pigments, discovered in various Paleolithic sites, suggest early humans used colour for decorative purposes or even ritualistic practices, revealing complex social behaviours and traditions.6
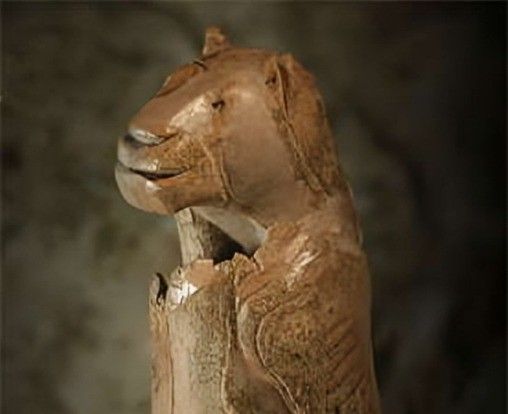

The "Lion Man" figurine from Germany, carved from mammoth ivory, represents one of the earliest examples of anthropomorphic art, showcasing advanced cognitive abilities in prehistoric humans.
The cave of Altamira in Spain houses stunning polychrome paintings of bison, believed to be 36,000 years old, demonstrating Paleolithic people's artistic skills and spiritual beliefs.7
Some of the earliest known tools discovered at the Gona site in Ethiopia exhibit advanced knapping techniques, indicating early humans' adaptability and innovation in tool-making for survival.8
In 2010, archaeologists in Indonesia unearthed the world's oldest known rock art, etched over 40,000 years ago, showcasing early humans' desire for artistic expression across different continents.9
Paleolithic burial sites, often accompanied by grave goods, suggest early humans practised death rituals, offering insights into their beliefs about the afterlife and honouring the deceased.10
Stonehenge, though from the Neolithic era, showcases early humans' incredible engineering skills and social complexity, manipulating massive stones to create lasting structures for unknown purposes.11
The cave art at Pech Merle in France includes rare human handprints, thought to symbolize identity or participation in rituals, demonstrating a sense of belonging among prehistoric people.12
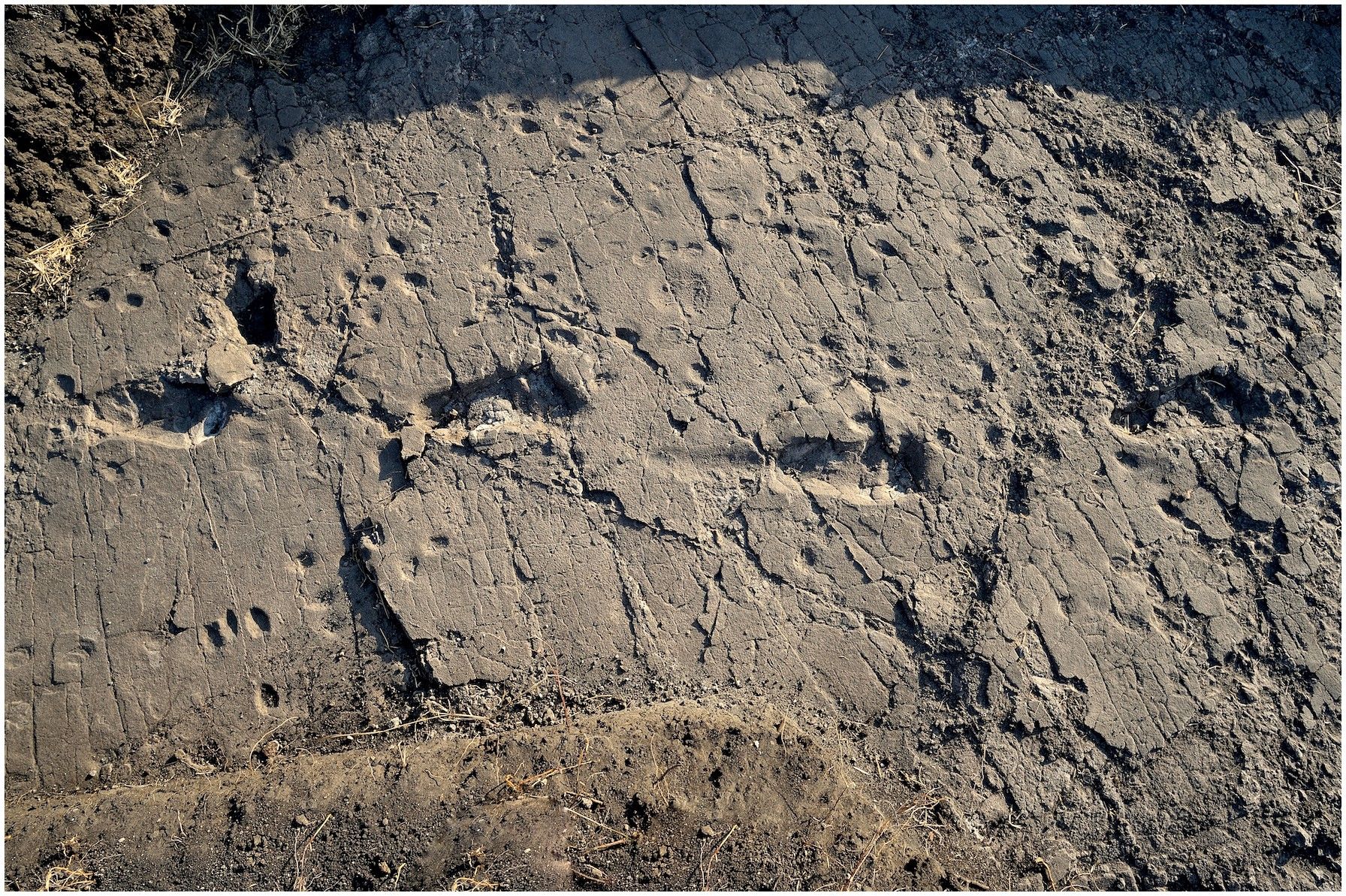

Fossilized footprints discovered in Laetoli, Tanzania, reveal that early hominins walked upright around 3.6 million years ago, offering critical evidence of early human evolutionary development.
Excavations at Dolní Věstonice in the Czech Republic uncovered ceramic figurines dating back to 29,000 years, showcasing early humans' creativity and the emergence of pottery techniques.13
The discovery of a fingerbone in Denisova Cave, Russia, led to the identification of a previously unknown human species, the Denisovans, highlighting the complexity of early human ancestry.14
Recent studies suggest prehistoric art, particularly its colours and symbols, likely served specific functions, possibly communicating information about food sources, dangers, or social structures.15
Paleolithic discoveries from different regions reflect diverse cultural expressions, highlighting how early humans adapted to their environments and developed unique artistic and practical traditions.16
The study of Paleolithic artifacts fascinates researchers, offering glimpses into early humans' creativity, survival strategies, and the cultural foundations of human civilization.17