“
The Indus Script remains one of the most captivating enigmas in the study of ancient languages. Originating from the Indus Valley Civilization, this script has long puzzled scholars due to its undeciphered nature. In this article, we present 15 fascinating facts about Indus Script and the ongoing efforts to decode this ancient language, offering insights into its complexity and significance.1
1
”
The Indus Script, created by the Indus Valley Civilization, is the earliest known writing system in the Indian subcontinent. Its origins and language remain unclear, as it is undeciphered and lacks bilingual texts. 1
The earliest examples of the Indus Script appear during the early Harappan phase (c. 3500-2700 BCE) on Ravi and Kot Diji pottery from Harappa, featuring single signs. These instances reflect an initial stage of script development. 2
Indus writing has been discovered on a variety of materials, including seals and seal impressions, pottery, bronze tools, stoneware bangles, bones, shells, ladles, and small tablets made from steatite, bronze, and copper.3
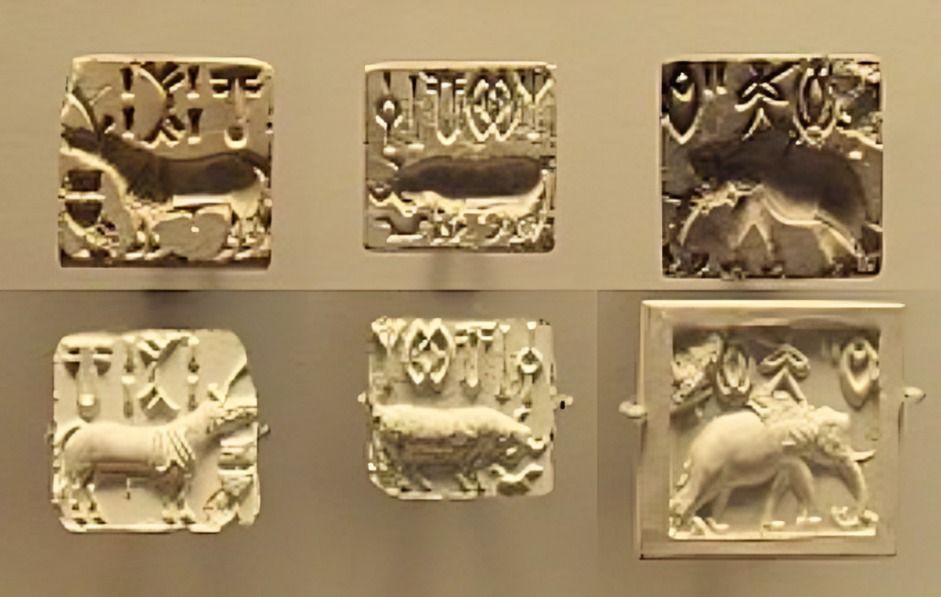

Square stamp seals are the primary medium for Indus writing, typically measuring about an inch (2.54 centimeters) square. These seals feature the script on the top and an animal motif in the center.
The Indus Script was used in narrative imagery, combining script with depictions of humans, animals, and imaginary creatures in active poses. These scenes are often related to myths or stories, resembling the religious, liturgical, and literary uses. 4
The Indus Script consists of slightly over 400 basic signs, but only 31 of them appear more than 100 times, while the majority were used infrequently. This uneven frequency suggests that some signs were more central to the script's usage than others.5
Several factors hinder the decipherment of the Indus Script. Unlike languages such as Egyptian, which were deciphered through bilingual inscriptions, no such inscriptions have been found for the Indus Script, making comparison to known writing systems impossible.6
The Indus Script was primarily written from right to left. However, some examples exhibit bidirectional writing, where the direction alternates between lines, with one line written in one direction and the next in the opposite direction. 7
Certain numerical values in the Indus Script are represented by specific symbols. A single unit is shown with a downward stroke, while units of ten are depicted using semicircles. 8
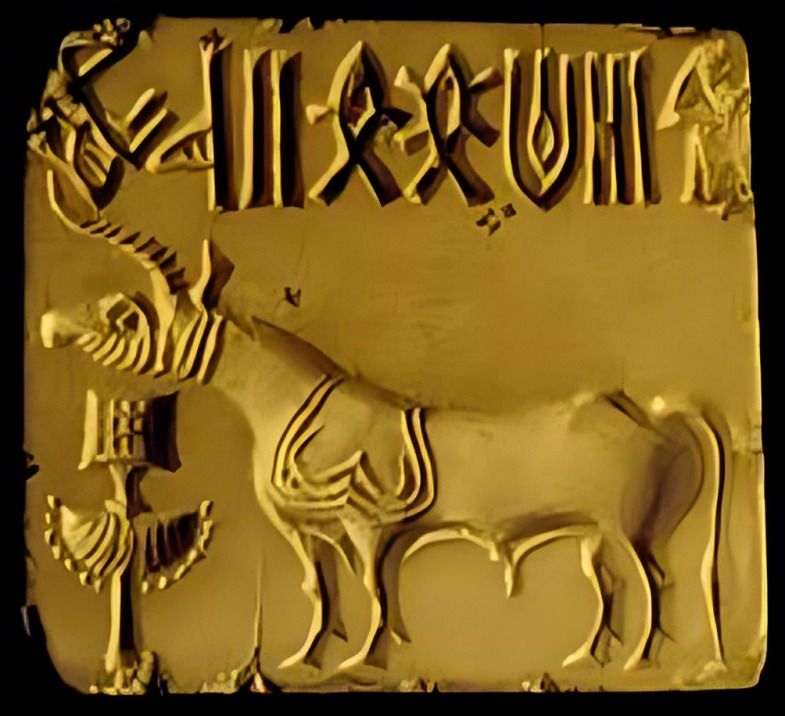

The Indus Script combined both word signs and symbols with phonetic value. This type of writing system is known as "logo-syllabic", where some symbols express ideas or words while others represent sounds.
By 1800 BCE, the Indus Valley Civilization began to decline, and with it, the use of their script started to fade. As civilization waned, so did their writing system. This gradual disappearance marked the end of one of the earliest writing traditions. 9
Scientists have identified specific numerical values in the Indus Script. A single unit is depicted with a downward stroke, while units of 10 are represented by semicircles.10
Several theories exist about the linguistic nature of the Indus Script, including its potential use for administrative purposes or religious texts. However, no definitive theory has been proven. The script’s true nature remains a subject of debate. 11
Modern technology, including computer analysis and statistical methods, has been used to study the Indus Script. Despite these advances, the script remains undeciphered. Ongoing research continues to explore its mysteries. 12
Some scholars speculate that the Indus Script might be linked to Dravidian languages or other language families. However, no conclusive evidence connects the script to any specific language group. This speculation adds to the script’s mystery. 13