“
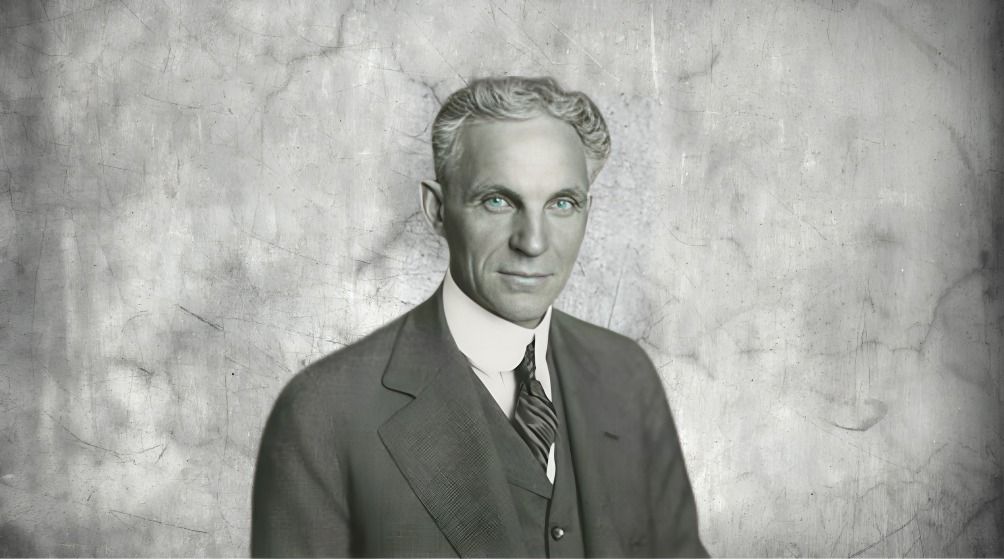
Henry Ford, the visionary founder of Ford Motor Company, reshaped the automotive industry with groundbreaking ideas and innovative strategies. From pioneering the assembly line to his bold business decisions, Ford's influence extended far beyond automobiles. His contributions to manufacturing, labor practices, and the development of affordable cars helped create the modern automobile industry. In this blog, we explore 20 fascinating facts about Henry Ford, shedding light on his lasting legacy, unconventional beliefs, and the profound impact he had on society.1
1
”
In 1914, Ford introduced the $5 per day wage, doubling the standard rate and improving workers' living conditions. This progressive wage system was instrumental in shaping future industrial labor practices. 1
Ford worked for Thomas Edison’s electric company, where he became friends with Edison. This relationship greatly influenced Ford’s mechanical expertise and future innovations in the automotive industry. 2
Ford's Model T, introduced in 1908, was the first affordable automobile for ordinary Americans. It revolutionized transportation, making car ownership accessible to the general public and reshaping society. 3
In 1913, Ford introduced the moving assembly line. This innovation boosted production speed and reduced costs, making cars more affordable and changing manufacturing methods worldwide. 4
Ford explored alternative materials like soybeans and hemp in his car manufacturing. He sought eco-friendly alternatives to traditional materials, focusing on renewable resources for more sustainable vehicles. 5
Ford created Greenfield Village in 1929, a living museum preserving American history. The museum showcases historical buildings and technologies, emphasizing the importance of preserving American heritage for future generations.
Ford’s innovations in mass production and interchangeable parts set global standards. His methods revolutionized manufacturing, influencing industries worldwide by improving efficiency and standardizing production techniques.6
Although admired for his achievements, Ford faced controversy for publishing anti-Semitic content. Ford’s anti-Semitic writings in the 1920s sparked criticism, but he later apologized, acknowledging the harm caused by his actions. 7
Ford’s work made automobiles affordable, helping create a consumer-driven economy. His contributions played a major role in reshaping American society and the global economy. 8
By making the Model T affordable, Ford helped create the American middle class. He enabled many to own cars and secure well-paying jobs, reshaping the economy and society in the process. 9
Ford created a research laboratory to advance car design and manufacturing technologies. The lab contributed to breakthroughs in engine design and alternative fuels, helping Ford stay ahead of the competition. 10
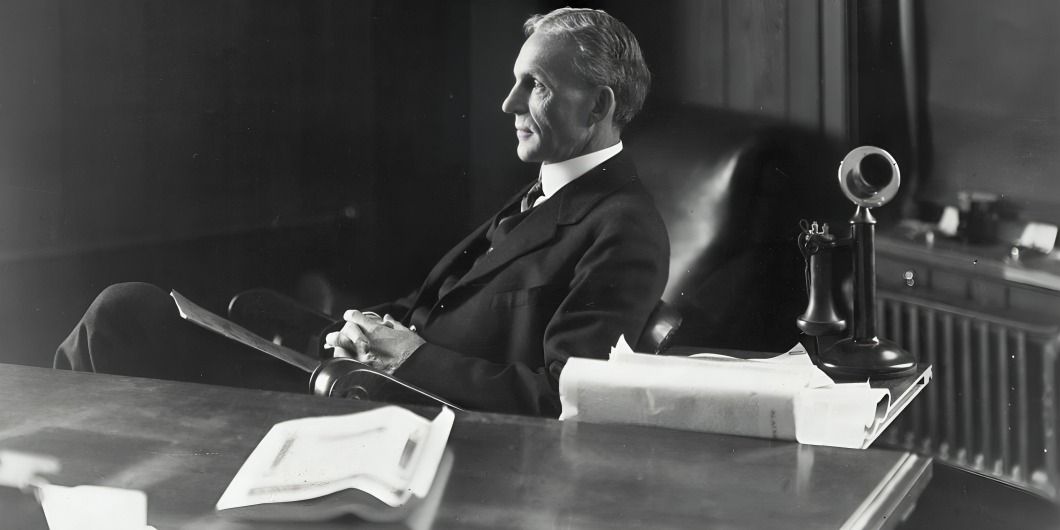

Ford transformed not only the automobile industry but business itself. By introducing mass production techniques, he set the global standard for manufacturing efficiency, revolutionizing how products were made across industries.
Ford’s labor practices were ahead of his time. He paid his workers higher wages, offered benefits, and improved factory conditions, influencing labor standards and worker rights worldwide. 11
Even after retiring in 1945, Ford stayed involved with his company. He continued to guide the company’s direction and influence its operations until his death in 1947, maintaining a strong legacy. 12
By 1927, Ford had sold over 15 million Model T cars. This made the Model T the best-selling car of its time, revolutionizing the automobile market and setting new industry standards.13
Ford aimed to improve everyday life through affordable products. His focus on innovation sought to make technology accessible and beneficial to ordinary people, helping improve the quality of life for many. 14

Ford later focused on the environmental impact of industrialization. He pushed for sustainable practices and explored methods to reduce his factories’ carbon footprint, anticipating future environmental concerns in manufacturing.
Ford’s relationship with Thomas Edison greatly influenced his career. Edison’s mentorship helped Ford develop many of his groundbreaking automotive ideas and innovations. 15
In 1915, Ford organized the "Peace Ship," an initiative to mediate between warring nations during World War I. He was passionate about peace and global harmony. 16
Ford founded the Ford Foundation in 1936, which became a major philanthropic organization supporting education, social welfare, and community development worldwide. 17


