“
Whether you're a concerned parent, a seasoned traveler, or simply looking to be prepared for unexpected emergencies, understanding the fundamentals of first aid is invaluable. This article delves into 20 essential facts about first aid manual tips—covering everything from basic CPR techniques to handling severe injuries and recognizing critical symptoms. Each fact is designed to empower you with the knowledge needed to respond effectively in various emergencies. By the end of this guide, you'll be equipped with actionable insights that can make a real difference when every second counts.1
1
1
”
Ensure the area is safe before giving aid. Look for hazards like traffic, fire, or unstable structures that could pose risks. Making sure the environment is secure helps prevent additional injuries and keeps both you and the injured person safe. 1
Call emergency services immediately if the situation is serious before starting first aid. Provide clear details about the incident and follow instructions given. This ensures professional help arrives quickly. 2
Approach the person gently and ask loudly, "Are you okay?" Tap their shoulder to check for responsiveness. Helps you determine their level of consciousness and understand their immediate needs, guiding the appropriate next steps for their care.3
If the person is unconscious, tilt their head back slightly and lift their chin to open the airway. Check for breathing for up to 10 seconds. Ensuring the airway is clear is crucial for effective breathing and oxygen flow. 4
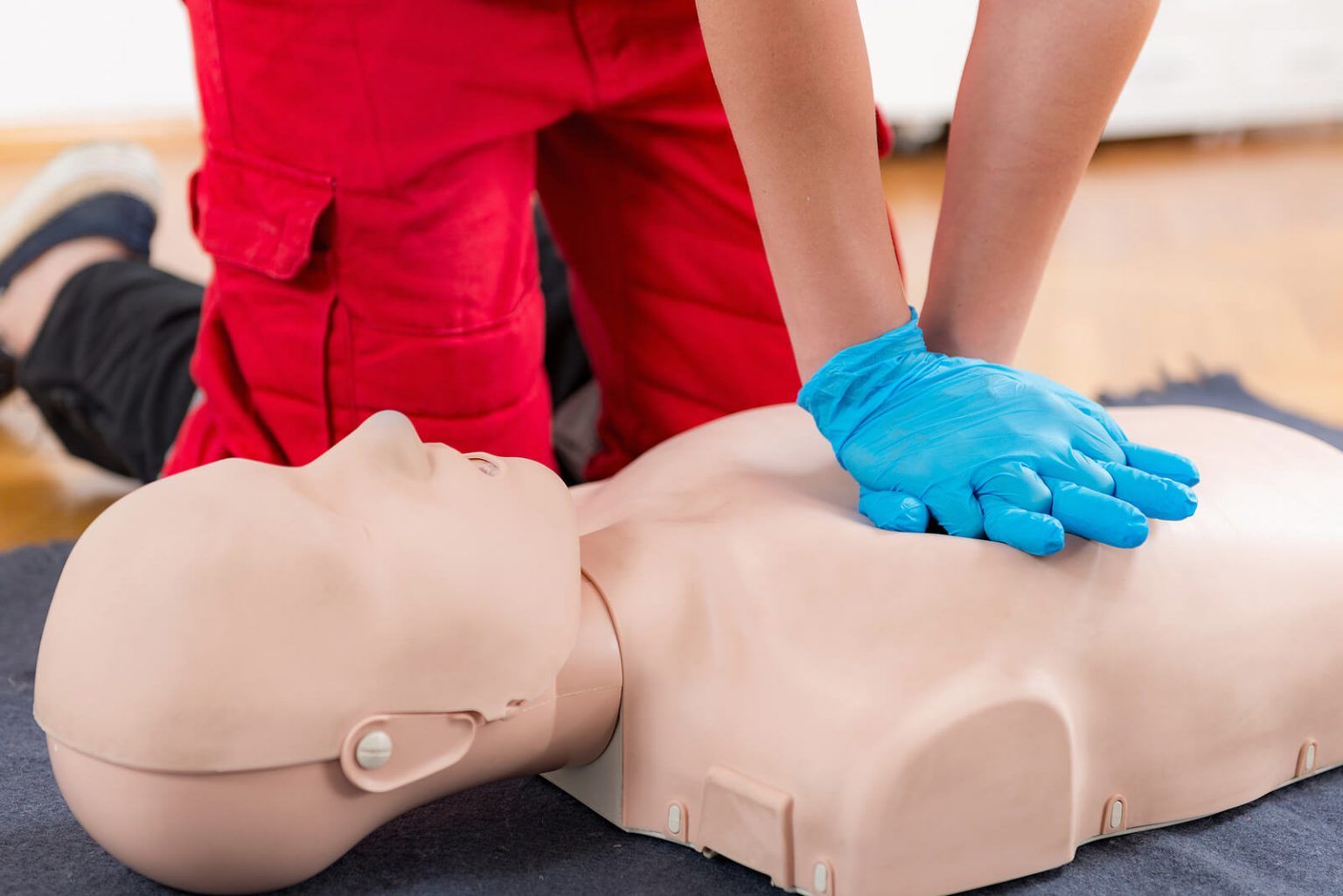
Start CPR immediately if the person is not breathing normally. Perform chest compressions by pressing hard and fast on the center of the chest. Proper CPR can save lives during critical moments of cardiac arrest.
If an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) is available, turn it on and follow the prompts. Attach the pads to the person’s chest as instructed and deliver a shock if advised. An AED can help restore a normal heart rhythm in emergencies. 5
Apply direct pressure to the wound with a clean cloth or bandage. Elevate the injured limb above heart level, if possible, to reduce blood flow, helps control bleeding and prevent shock by minimizing blood loss and stabilizing the situation. 6
In the event that someone is feeling faint or has fainted, lay the person down, slightly elevate their legs, and cover them with a blanket to keep warm. Monitor their breathing and offer reassurance until help arrives. 7
Cool a burn with cool (not cold) running water for at least 10 minutes. Cover the burn loosely with a sterile dressing to protect it from infection. Proper burn care reduces pain and lowers the risk of complications. 8
f something is in the eye, do not rub it. Flush the eye with clean water or saline solution. For chemical exposure, rinse with water continuously and seek medical help. Quick action is crucial to prevent serious eye damage. 9
During a seizure, move objects away and do not restrain or put anything in their mouth. Time the seizure and stay with the person until it ends. Ensuring safety helps prevent additional injuries and ensures their well-being. 10
Rest the injured limb and apply ice wrapped in a cloth for 15-20 minutes each hour. Use an elastic bandage to compress and elevate the limb above the heart level. This approach helps manage pain and reduces swelling effectively. 11
In the event of heatstroke, move the person to a cooler place and use cool, wet clothes or a cool bath to lower their body temperature. Offer small sips of water if they can swallow. 12
In the event of hypothermia, remove wet clothing and cover the person with dry blankets or warm clothing. Gradually warm them with dry heat, such as blankets or warm drinks. 13
If the person has an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) and is experiencing a severe allergic reaction, administer it immediately. Seek medical help promptly. Using the auto-injector can be lifesaving in severe allergic reactions. 14
For a nosebleed, have the person sit upright and lean slightly forward. Pinch their nostrils with a tissue or cloth for 10-15 minutes until the bleeding stops. This technique helps control the nosebleed and prevents excessive blood loss. 15
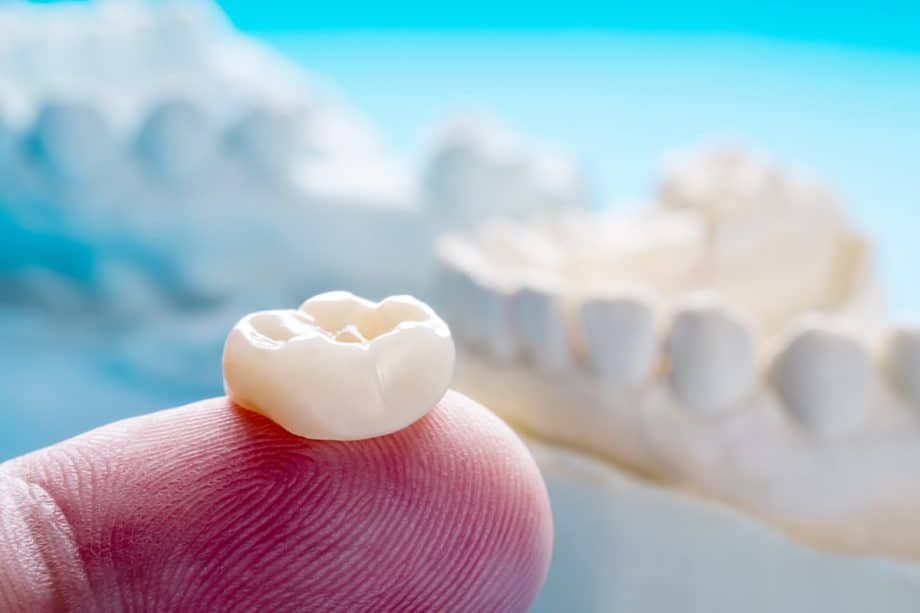
If a tooth is knocked out, handle it by the crown, rinse it with water if dirty, and try to reinsert it into the socket. If that’s not possible, store the tooth in milk and seek dental care immediately to increase the chance of saving it.
If bitten by a snake or animal, keep the person calm and still. Wash the bite area with soap and water, and immobilize the affected limb at or below heart level. Seek medical help immediately for proper treatment and care. 16
In the event of a stroke, look for signs such as facial drooping, arm weakness, or speech difficulties. Call emergency services immediately if any symptoms are present. 17
After providing initial first aid, continue monitoring the person’s condition until medical professionals arrive. Share all relevant information with emergency responders to ensure continuity of care and help them provide the best treatment possible. 18


