“
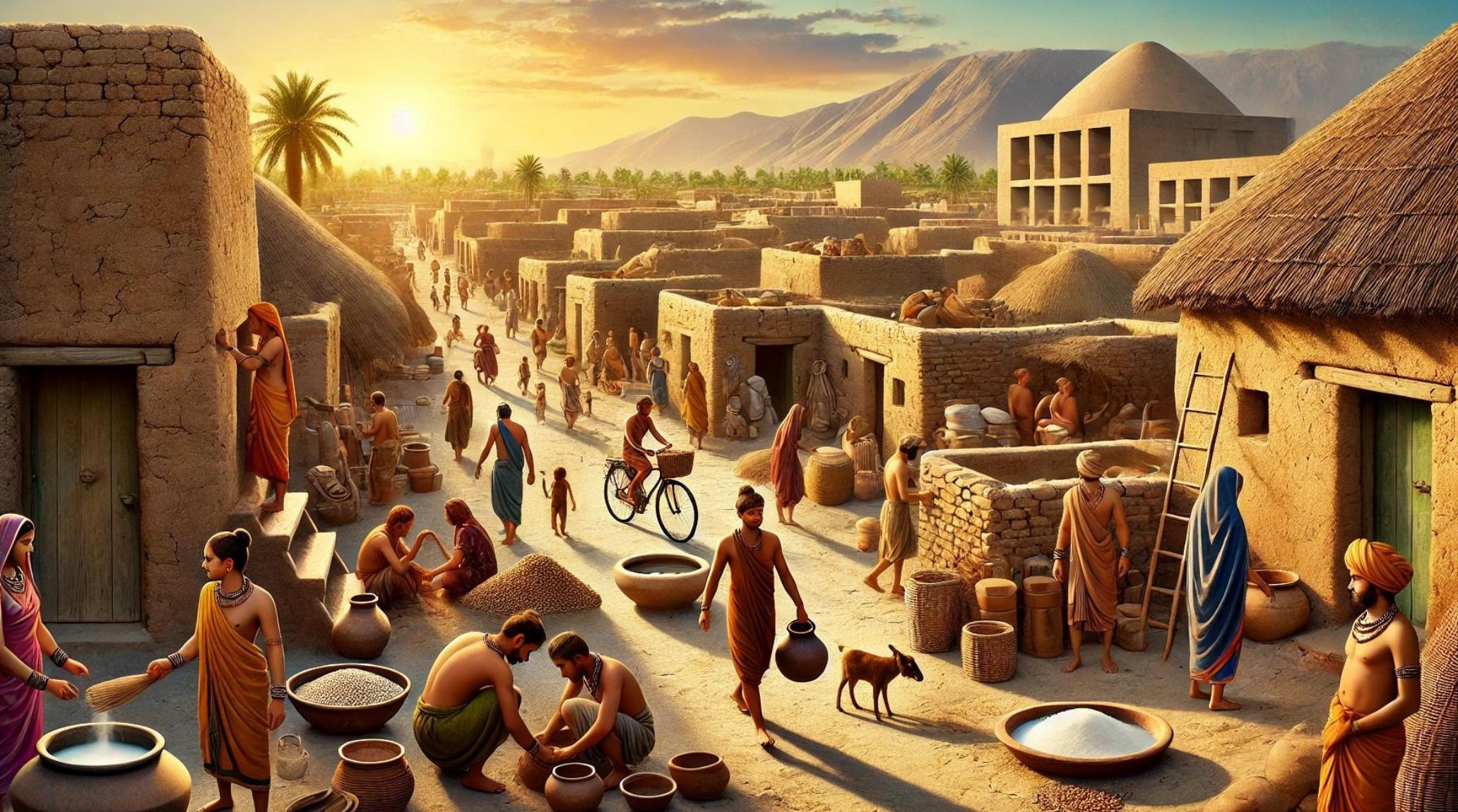
Daily life in Ancient Egypt was as diverse as the civilization itself. From bustling marketplaces to serene temples, the ancient Egyptians had a rich daily routine filled with unique practices and societal roles. In this article, we explore 20 fascinating facts about how the ancient Egyptians lived their everyday lives.1
1
”
Daily life in Ancient Egypt varied by social class, influencing one's work and lifestyle. Most Egyptians dressed in simple linen garments, ate primarily grains, vegetables, and beer, and engaged in sports and board games. 1
The Nile River was the lifeblood of Ancient Egypt. Its annual flooding deposited nutrient-rich silt on the fields, ensuring abundant crops. Egyptians developed complex irrigation systems to manage the water. 2
Ancient Egyptians used a complex system of pictorial writing known as hieroglyphics. This script combined logographic and alphabetic elements and was primarily used in religious and monumental contexts.3
Egyptian society was highly stratified. At the top was the Pharaoh, believed to be a god, followed by priests, nobles, and scribes. Farmers, laborers, and slaves formed the lower classes, with distinct roles and limited mobility.4
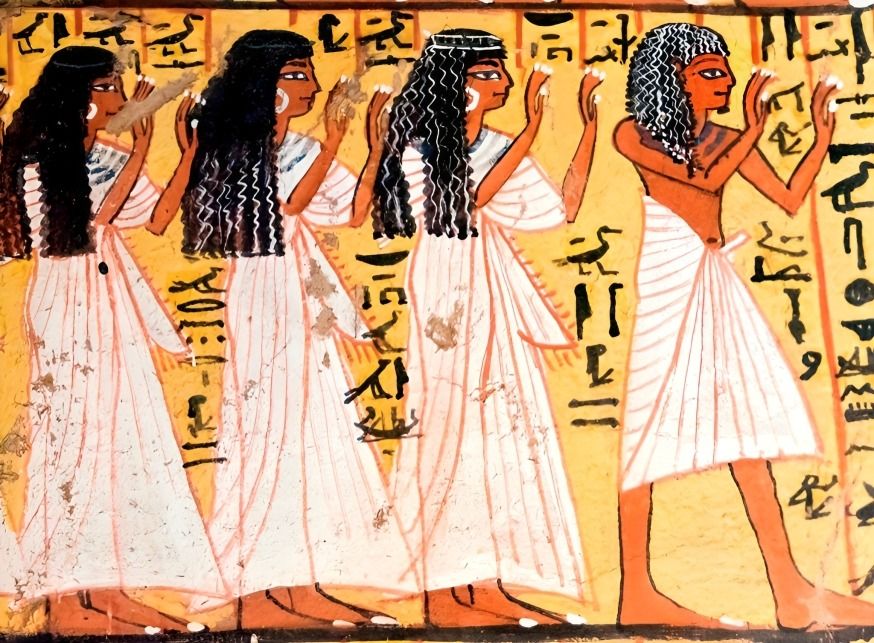

Egyptians wore linen garments due to the hot climate. Men typically donned kilts or loincloths, while women wore long dresses. Both males and females were often accessorized with jewelry made of gold, beads, and semi-precious stones.
Family was central to Egyptian life, and marriages were usually arranged. Women had substantial rights, including owning property and initiating divorce. Children were cherished, and family life was considered essential for happiness.5
The ancient Egyptian diet consisted mainly of bread, beer, onions, and fish. Wealthier Egyptians enjoyed a more varied diet including meat, poultry, and fruits. Honey was used as a sweetener, and spices were imported from abroad. 6
Egyptians placed high importance on personal hygiene and appearance. Both men and women used oils and perfumes, and makeup was common. Kohl was applied around the eyes, believed to protect against the sun and evil spirits. 7
Most ancient Egyptians lived in mud-brick houses with flat roofs. These homes were typically single-story structures with small, interior courtyards. Wealthier Egyptians had more elaborate homes with gardens and multiple rooms. 8
Scribes held a prestigious role, as literacy was rare. They underwent rigorous training in reading and writing hieroglyphs. Scribes were essential for record-keeping, administration, and literary works. 9
Religion was integral to Egyptian life, with numerous deities worshiped in daily rituals. Temples were centers of worship and were richly decorated. Priests conducted rituals to honor gods and ensure the stability of the cosmos. 10
Egyptians believed in an afterlife, leading to elaborate burial practices. Bodies were mummified to preserve them for the journey to the afterlife. Tombs were filled with goods, food, and amulets for use in the next world. 11
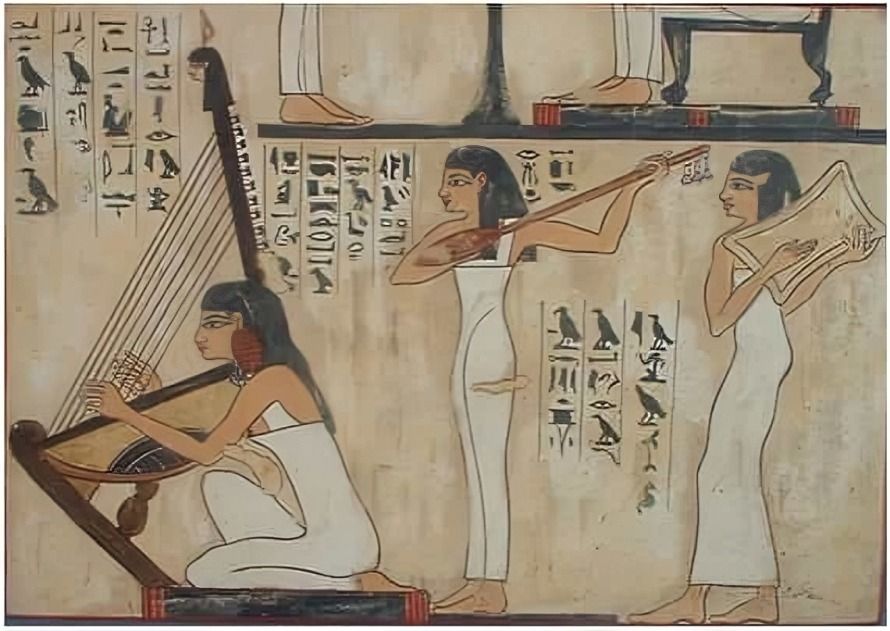

Egyptians enjoyed various forms of entertainment, including music, dance, and board games. Senet, a game resembling chess, was popular among all social classes. Festivals with music and dancing were also common.
Skilled artisans produced exquisite crafts such as pottery, jewelry, and textiles. Pottery was used for both practical and ceremonial purposes, while jewelry often featured intricate designs and hieroglyphs. 12
Farming in ancient Egypt involved simple tools like hoes and sickles. The plow, which was sometimes drawn by oxen, helped till the soil. Farmers worked intensively during the planting and harvesting seasons. 13
Ancient Egyptian medicine combined practical treatments with spiritual practices. Physicians used herbal remedies, surgeries, and magical spells. Medical texts on papyrus reveal knowledge of anatomy and disease.14
The Nile River was a major transportation route. Egyptians used boats and ships for travel and trade. Donkeys and carts were commonly used for land transport, particularly in farming and trade activities. 15
The construction of monumental structures, like the pyramids and temples, required vast labor forces. These projects were often undertaken as part of state or religious duties and involved intricate planning and organization. 16
Egypt’s economy was bolstered by trade with neighboring regions. Goods like gold, papyrus, and linen were exported, while incense, myrrh, and other luxury items were imported. Trade routes extended into Africa, the Near East, and beyond. 17
Gender roles in Egypt were relatively defined, but women had more rights compared to many ancient cultures. Marriage was a social contract, and women could manage households, inherit property, and participate in legal contracts. 18