“
The muscles and skeletal system are crucial for movement, stability, and overall body structure. This blog will uncover 20 fascinating Muscles and Skeletal System Facts. These facts highlight how muscles and bones interact to enable movement, support the body, and maintain posture. 1
1
1
1
1
”
The adult human body contains 206 bones that form the skeleton, providing structure, protection for organs, and enabling movement. The bone count can vary due to natural differences and the fusion of certain bones over time. 1
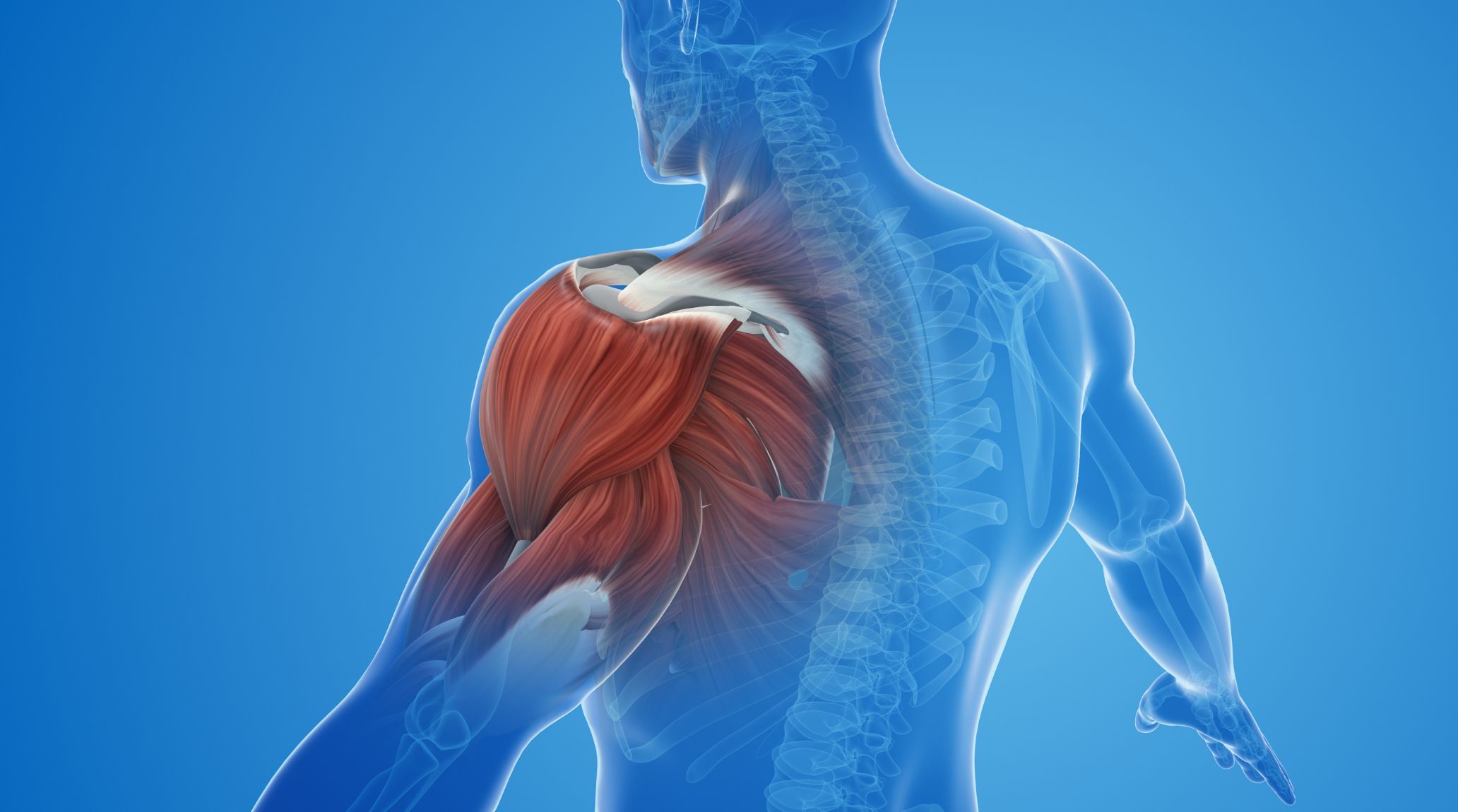
Muscles are divided into three types: smooth, cardiac, and skeletal. Smooth muscles work involuntarily in organs, cardiac muscles power the heart, and skeletal muscles attach to bones, enabling movement and daily physical activities. 2
Sharks and rays have skeletons made entirely of cartilage, not bone. This flexible, lightweight tissue allows them to swim with agility, perfectly suited for deep-sea environments and enhancing their maneuverability. 3
The masseter, located in the jaw, is the strongest muscle in the human body. It exerts up to 250 pounds of force, highlighting its essential role in chewing food and aiding the digestive process. 4
Human bones are incredibly strong and able to withstand forces up to 250 pounds per square inch. This strength makes them comparable to concrete, playing a crucial role in supporting and protecting the body. 5
While men's and women’s skeletons are generally similar, a woman’s pelvis is uniquely adapted for childbirth. Its distinct shape, size, and angle help facilitate the birthing process, making it different from a male pelvis. 6
The body contains over 600 muscles, responsible for movement, maintaining heartbeat, and aiding digestion. These muscles work in coordination with 206 bones, enabling us to perform everyday activities and maintain overall health. 7
Bones grow throughout childhood and adolescence, with growth plates closing around age 25, marking the end of skeletal development. After this, bones maintain their strength but stop increasing in length. 8
The stapes, located in the middle ear, is the smallest and lightest bone in the human skeleton. Despite its size, it plays a critical role in hearing by transmitting sound vibrations to the inner ear for processing. 9
Muscle cramps are involuntary muscle contractions caused by dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, or overuse. These painful episodes highlight the importance of proper hydration and balanced electrolytes to maintain muscle function. 10

Your teeth are part of your skeleton, containing calcium-like bones. However, unlike bones, teeth lack collagen, which provides flexibility. This makes teeth more rigid and less flexible, but crucial for chewing and speaking.
The femur is the strongest and longest bone in the human body. It supports up to 1,200 pounds of weight and plays a key role in bearing the body’s weight, facilitating movement and overall mobility. 11
Exoskeletons support weakened bones and joints, helping individuals with arthritis or spinal injuries. These devices enhance mobility and strength, improving the quality of life for those facing physical challenges. 12
Muscles make up about 40% of body weight in men and 35% in women. This difference reflects the critical role muscles play in physical strength, body composition, and overall mobility in both genders. 13
Bones have an incredible ability to heal themselves. When a bone fractures, specialized cells called osteoblasts generate new bone tissue, helping the bone mend naturally and regain strength over time. 14
Evel Knievel, famous for motorcycle stunts, sustained 433 bone fractures by 1975. A failed shark jump in 1976 gave him a concussion and two broken arms, leading to his retirement and passing the torch to his son, Robbie. 15

Xiao Lin from China set a world record for the most muscle-ups in one hour, completing 402 in November 2021. His incredible strength and endurance demonstrated his dedication to fitness, solidifying his place in the record books.
The first recorded treatment for muscle injuries dates back to ancient Greece around 400 BCE. Hippocrates, considered the father of medicine, described techniques like rest and manual therapy to aid recovery from muscle strains. 16
Bone injury treatments date back to ancient Egypt around 3000 BCE. Early methods, including splints made of wood and linen, were used to immobilize fractured bones, laying the foundation for modern orthopedic practices. 17
Muscles have a rich blood supply, allowing them to heal faster than other tissues like bone or tendon. This enhanced circulation helps muscles recover quickly from stress and injuries, unlike less vascularized tissues. 18


