“
The brain and nervous system are essential for controlling every aspect of our bodies, from basic reflexes to complex cognitive functions. In this blog, we'll explore 20 intriguing Brain and Nervous System Facts that reveal the astonishing intricacies of these vital systems. Discover how the brain processes information, how neurons communicate, and other unique details that showcase the incredible complexity of our neural networks. Whether you're a science lover or simply curious about how your body functions, these facts will deepen your understanding and appreciation of the brain and nervous system.1
1
”
The human nervous system has two parts: the central nervous system (CNS), located in the skull and spine, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which includes all other nerves throughout the body. 1
The brain generates about 20 watts of electrical power while awake, enough to power a dim light bulb! This makes it one of the most energy-intensive organs, constantly processing and transmitting information. 2
The human brain contains approximately 86 billion neurons connecting to thousands of other neurons. This intricate network forms the basis for all thoughts, feelings, and actions, creating a complex communication web throughout the body. 3
Neurons have three main parts: the cell body, which houses the nucleus; dendrites, which receive signals; and the axon, which transmits impulses to other neurons or muscles, facilitating communication in the nervous system. 4
Nerve impulses can travel up to 120 meters per second, equivalent to about 268 miles per hour. This rapid communication is essential for reflexes and other immediate responses to stimuli. 5
Did you know that you're taller in the morning? After a night's sleep, your spinal discs rehydrate and expand, slightly increasing height. Gravity compresses these discs throughout the day, causing you to lose some of that height by evening. 6
The nervous system has two parts: the voluntary (somatic) system, which controls conscious movements, and the involuntary (autonomic) system, which manages automatic functions like heart rate and breathing without conscious control. 7
The brain's storage capacity is around 2.5 petabytes, equivalent to three million hours of TV shows! This immense capacity allows us to store vast amounts of information. 8
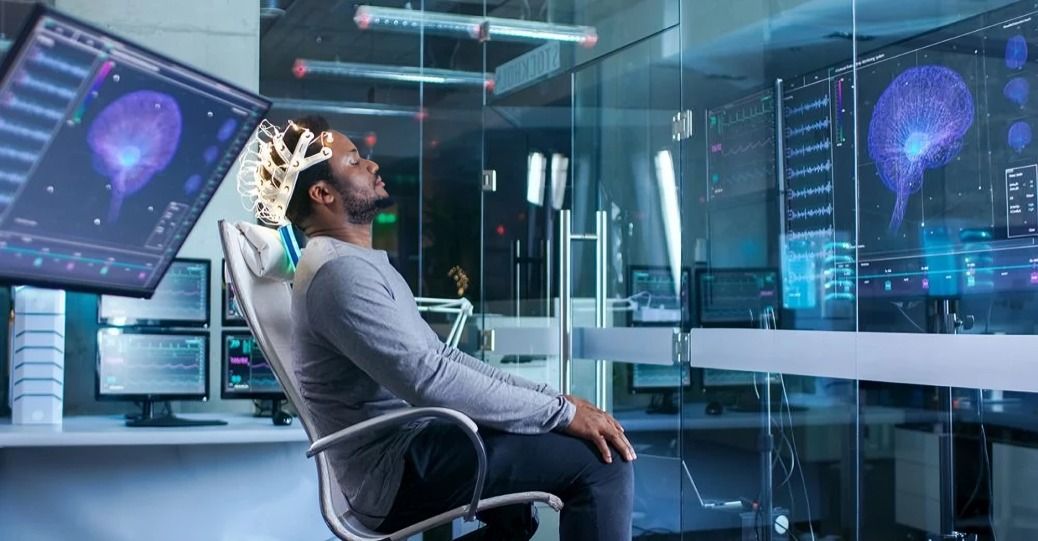

Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) let people control things like computer cursors and robotic limbs by thinking. New technology has made it possible to do even more, like interact with virtual environments, making life easier for those with disabilities.
While spinal traction dates back to ancient Egypt, the first documented spine surgery, a laminectomy, is credited to Paul of Aegina around 650 AD, marking a significant milestone in the history of medicine. 9
About 12% of people dream in black and white, while the rest experience vivid colors. Daily experiences influence this phenomenon and can vary from person to person, making dreams unique. 10
Men's spines average 71 cm and women's 61 cm, reflecting anatomical differences that influence body proportions, posture, and physical characteristics between genders, affecting how we carry ourselves and our overall appearance. 11
Neurons vary in shape and size based on their function. Sensory neurons have dendrites at both ends and a central cell body, while motor neurons have a cell body at one end and dendrites at the other. 12
One of the most cutting-edge techniques in spine surgery is the use of artificial intelligence (AI). AI-powered systems can analyze patient data, assist in surgical planning, and provide real-time guidance during procedures. 13
The average adult human brain weighs about 3 pounds, but its size does not correlate with intelligence. Interestingly, Einstein's brain was smaller than average, challenging conventional ideas about brain size and cognitive ability. 14
During deep sleep, the brain exhibits a pattern of electrical activity called delta waves. These waves are essential for restorative sleep and memory consolidation, allowing the brain to process and store daily information. 15
Astronauts often return slightly taller from space missions because the lack of gravity allows their spinal discs to expand. This temporary height increase reverses once they return to Earth and experience normal gravity. 16
The brain does not have pain receptors, meaning it cannot feel pain. However, it plays a vital role in processing pain signals from the rest of the body, influencing our perception of pain. 17

The hero shrew, a small African mammal, has a solid spine that can support human weight. This adaptation helps it navigate tough soil and face predators with remarkable resilience.
People are more likely to remember information presented in color, as the brain processes color differently than black and white. This colorful presentation enhances memory retention and makes learning more engaging and effective. 18


