“
Understanding & managing arthritis pain involves more than just treating aching joints—it requires a deep awareness of your body, lifestyle changes, and consistent care. Arthritis, which includes over 100 related conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, affects millions globally. Pain management isn’t just about medication; it includes exercise, nutrition, emotional well-being, and informed decision-making. 1
1
”
Arthritis pain often worsens due to joint inflammation triggered by immune dysfunction, overuse, or cartilage breakdown. Understanding this root cause is essential for tailoring treatments that reduce pain. 1
Weight management significantly reduces arthritis pain, especially in weight-bearing joints like knees and hips. Just 10 pounds of weight loss can relieve up to 40 pounds of pressure from your knees. 2
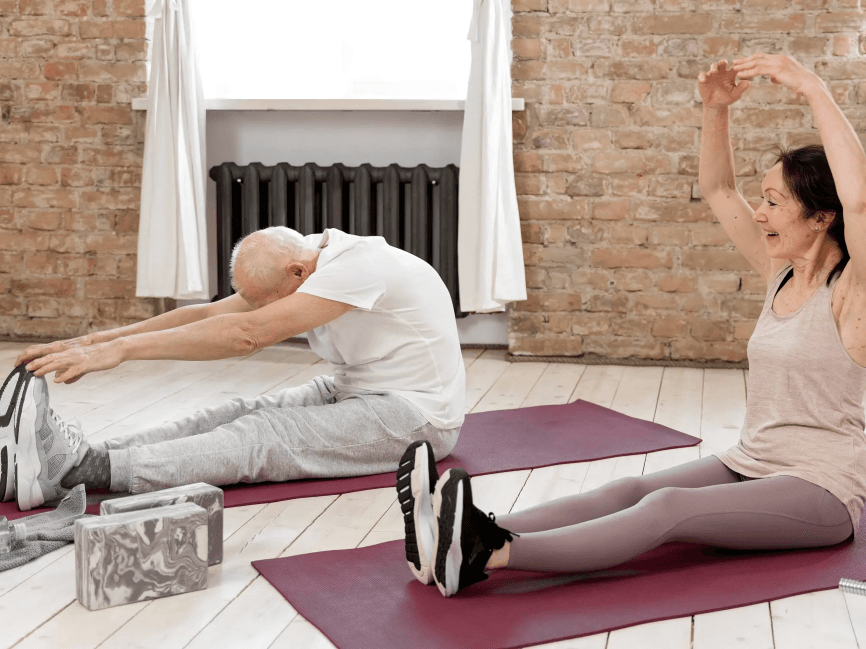

Joint stiffness in arthritis patients tends to peak in the morning. Gentle stretching and warm showers can help loosen joints and increase flexibility, reducing stiffness and pain throughout the day.
Omega-3 fatty acids from fish or flaxseeds have anti-inflammatory properties. Regular intake has been shown to reduce joint swelling and pain in individuals with rheumatoid or inflammatory arthritis. 3
Low-impact exercises such as swimming, tai chi, and walking enhance blood flow and flexibility without over-stressing joints. These movements are critical for preserving the range of motion. 4
In osteoarthritis, cartilage—the cushioning tissue between bones—gradually wears away. This leads to bones rubbing together, stiffness, and chronic discomfort over time if not properly managed. 5
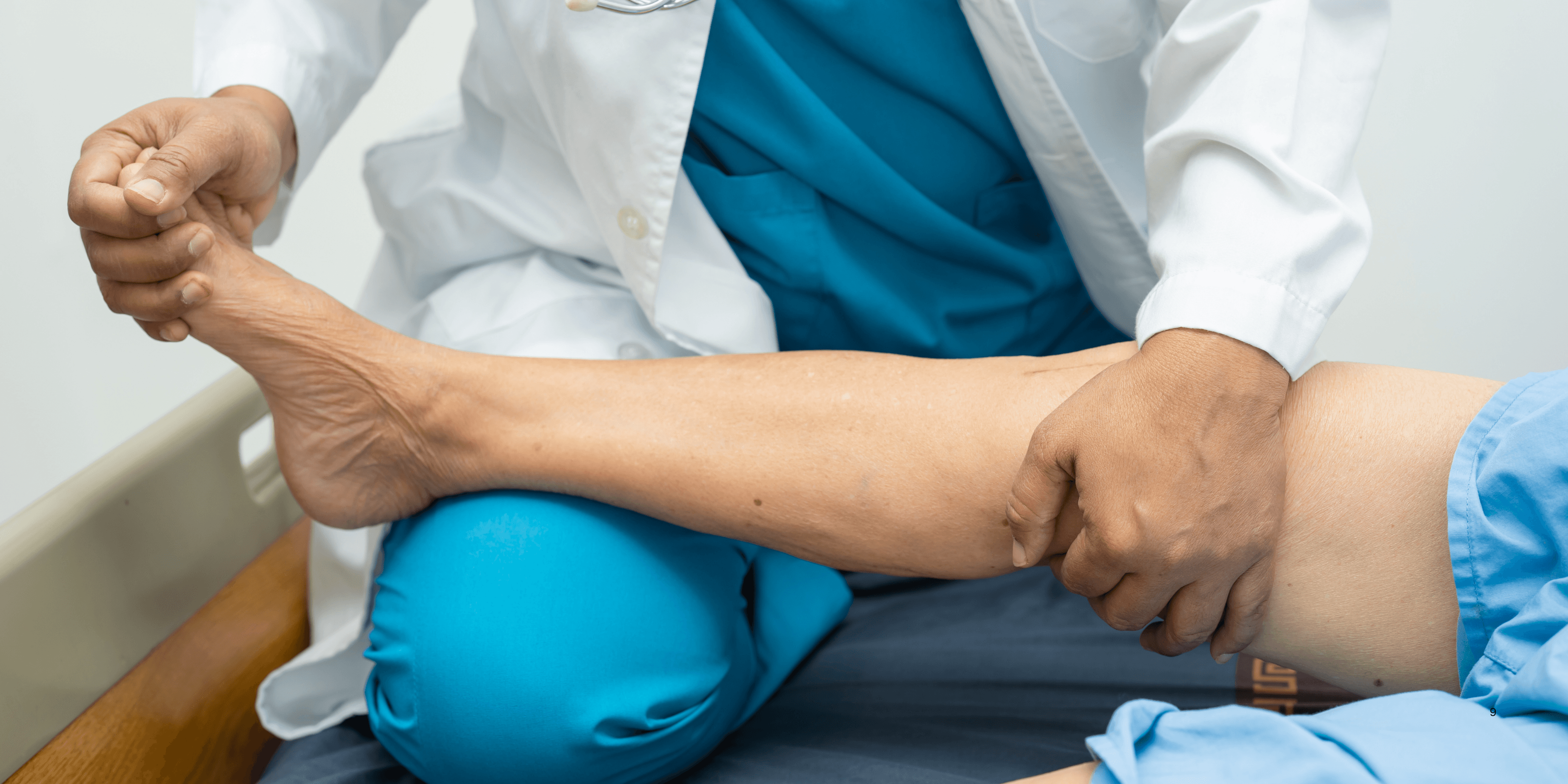
Physical therapy, when guided by specialists, helps strengthen muscles around affected joints, improves stability, and reduces stress on joints, making it a core component of effective arthritis pain management. 6
Prolonged inactivity can worsen arthritis symptoms by reducing joint lubrication and causing stiffness. Even light movement during the day is better than total rest for preserving joint health. 7
Pain perception in arthritis is also influenced by brain signals and emotional stress. Managing mental health with techniques like mindfulness and relaxation therapy can significantly reduce felt joint pain. 8
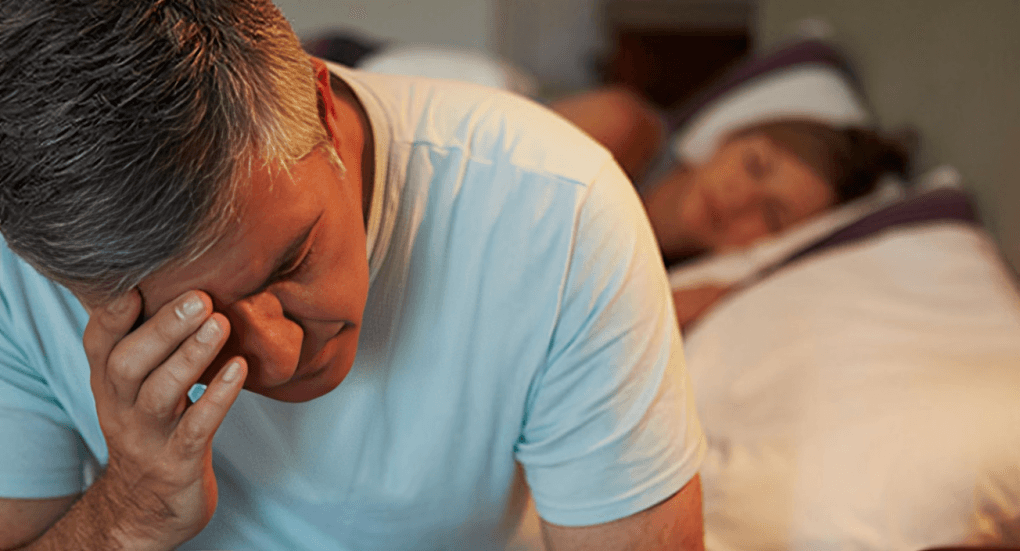

People with arthritis may experience fatigue from chronic inflammation. Managing sleep quality, reducing stress, and pacing daily tasks help conserve energy and improve overall comfort and functioning.
Anti-inflammatory foods like berries, olive oil, spinach, and turmeric can help ease arthritis symptoms when included regularly in meals. Diet plays a silent yet vital role in long-term joint health. 9
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen offer short-term relief but should be used with caution, as long-term use can affect stomach, kidney, and heart health in arthritis patients. 10
Joint-friendly tools, such as jar openers and ergonomic kitchen gadgets, can make everyday activities easier for arthritis sufferers, reducing pain from repetitive motions and preserving hand function. 11
Staying hydrated supports joint lubrication and reduces stiffness. Even mild dehydration can worsen arthritis symptoms, so consistent fluid intake is essential to maintaining joint mobility and reducing discomfort. 12
Smoking is linked to increased arthritis severity, particularly in rheumatoid arthritis, as it can increase inflammation. Quitting smoking supports joint health and treatment success. 13
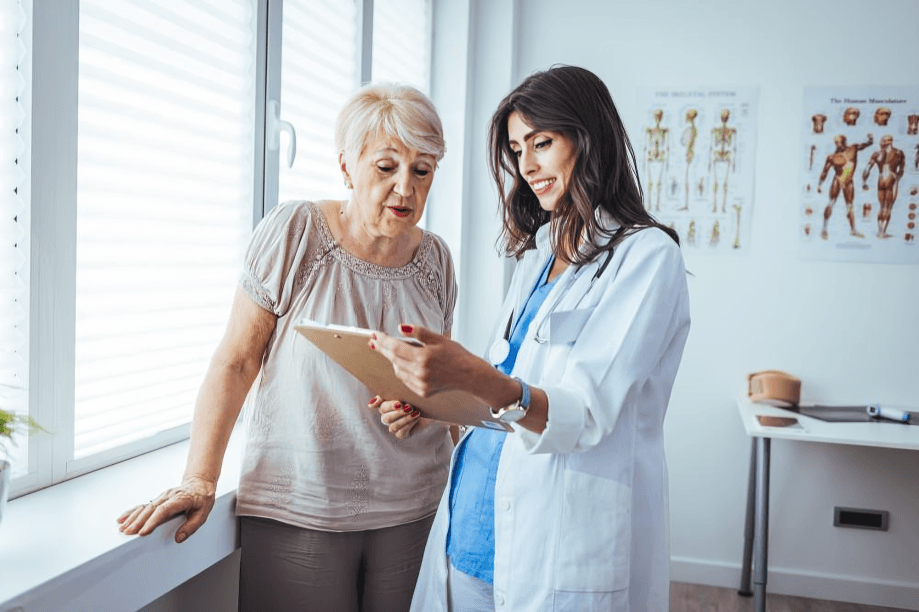

Regular doctor check-ups ensure arthritis treatment remains effective over time. Flare-ups, medication adjustments, or new symptoms require professional input to keep pain manageable.
Glucosamine and chondroitin are supplements some people use for osteoarthritis. While evidence is mixed, many patients report reduced pain, though they work best in the early stages. 14
Weather changes, particularly cold or damp climates, are known to intensify arthritis pain. While not fully understood, pressure changes can impact joint tissues and movement, which is important. 15
Arthritis can be isolating, but support groups offer emotional and practical help. Sharing experiences reduces stress and provides encouragement, which is vital in coping with chronic joint pain over time. 16
Philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche believed suffering could lead to strength. In arthritis care, resilience is often built through education and proactive treatment, transforming pain into powerful knowledge. 17


