“
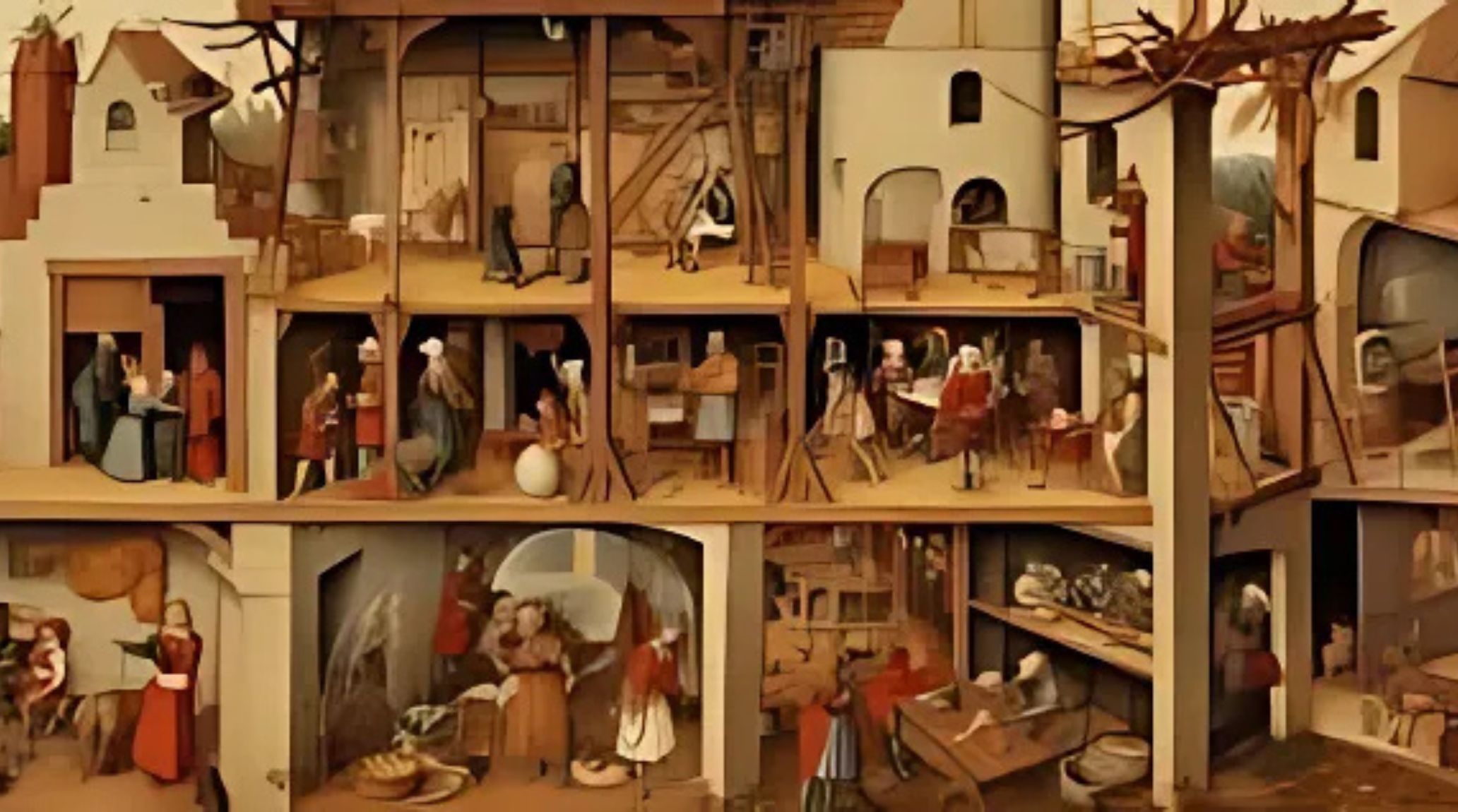
Medieval daily life varied greatly depending on social class, geography, and the period, but certain common elements shaped the experience for most people. For peasants, life was centered around agriculture, with long hours spent farming and tending to animals. Despite the hardships, religious faith was a constant, and festivals provided a break from daily routines. The medieval world was defined by a strict social hierarchy, communal living, and a close connection to the land.1
1
”
The feudal system structured medieval society, with peasants working the land for lords in exchange for protection and housing. It created a hierarchical society where lords held power over vast territories. 1
Towns burgeoned as trade hubs in the Middle Ages, bustling with markets where goods from distant lands were exchanged. They attracted artisans and merchants. Guilds regulated trades and maintained quality standards. 2

Guilds were instrumental in medieval society, organizing and regulating trades such as blacksmithing and carpentry. They ensured quality craftsmanship, managed apprenticeships, and protected the economic interests of their members.
Medical treatments in medieval times often relied on herbal remedies and superstitions. Surgery was considered a risky last resort due to limited knowledge. High mortality rates were common. 3
During the Middle Ages, education was primarily the responsibility of monasteries and churches. Monks taught Latin, theology, and basic literacy. They instructed novices and local children alike. 4
The medieval diet was simple yet hearty, consisting mainly of staples like bread, vegetables, and grains. Dairy products complemented these staples. Meat was reserved for special occasions. 5
Medieval clothing varied widely depending on social status and occupation. Nobles and wealthy merchants adorned themselves in fine fabrics like silk and velvet. Intricate embroidery and jewels showcased their wealth and status. 6
Entertainment included feasts, tournaments, and mystery performances depicting biblical stories. These events provided social interaction and cultural expression. They were highlights of medieval life. 7
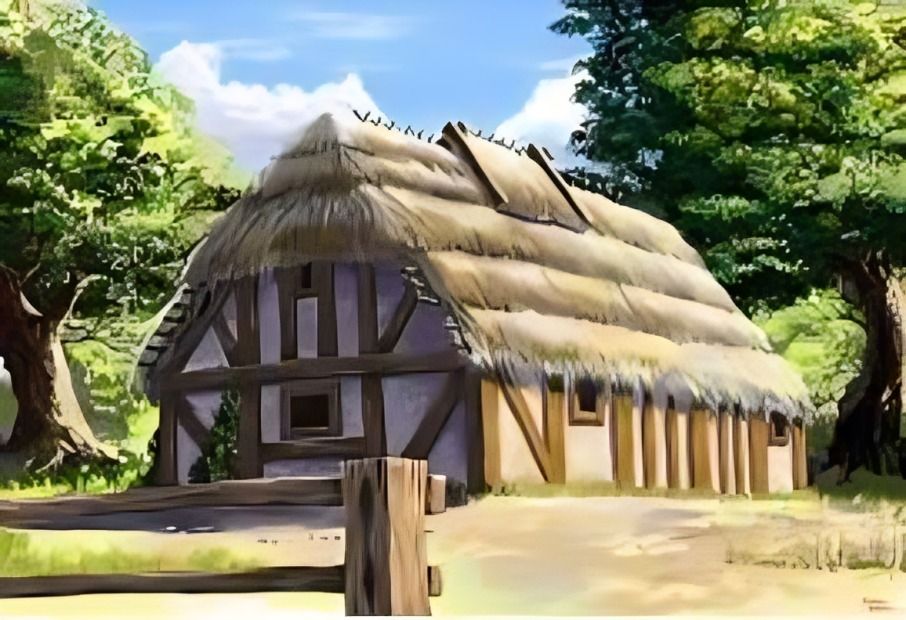

Peasants lived in modest homes made of wood and thatch. Nobles resided in stone castles with servants and guards. The contrast in living conditions was stark.
Women managed households, raised children, and sometimes worked alongside men in fields and crafts. Their roles were vital yet often undervalued. They contributed significantly to daily life. 8
Knights adhered to a code of chivalry, emphasizing honor, bravery, and loyalty to their lords. Protecting the weak was a key tenet. This code shaped their conduct and identity. 9
Markets were lively hubs of commerce where merchants traded spices, textiles, and other goods worldwide. These markets fostered economic growth. They were central to town life. 10
Daily life revolved around religious practices, with the Church influencing moral standards, education, and societal norms. The Church held significant power. It was central to community life. 11
Peasant life revolved around agricultural seasons, with planting and harvesting dictating daily tasks and festivities. Seasonal rhythms shaped their existence. Festivals marked important milestones. 12
Families were patriarchal, with multiple generations living together and contributing to farming and household chores. These extended families supported each other. They formed the core of medieval society. 13
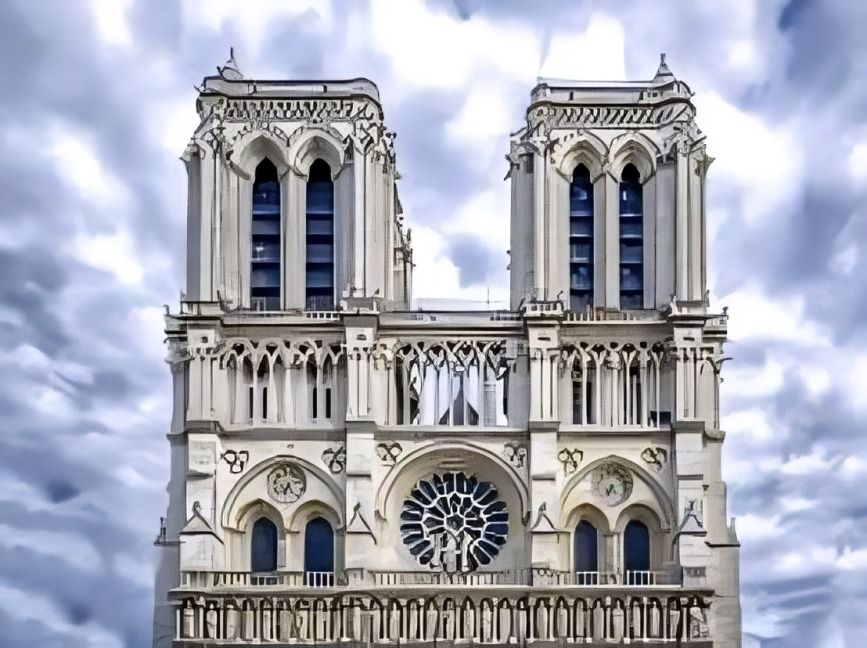

Gothic architecture flourished, with cathedrals serving as symbols of faith and showcasing intricate craftsmanship. These structures were engineering marvels. They inspired awe and devotion.
Hygiene practices were basic, with bathing considered both a luxury and a health risk due to limited access to clean water. Sanitation was rudimentary. It impacted health and lifestyle. 14
Astrology influenced daily decisions, while astronomy was studied for agricultural purposes and timekeeping. These sciences held practical and mystical significance. They guided medieval thought and practices. 15
The period left a lasting legacy on European culture, shaping institutions, governance, and social structures that continue to impact society today. Medieval influences persist. They are embedded in modern civilization. 16