
“
In today’s fast-paced world, facts about journaling for mental health is more than a soothing idea—it’s a daily practice with lasting benefits. From calming anxiety to boosting self-awareness, facts about journaling for mental health by offering clarity, confidence, and emotional release. It’s not about perfect writing—it’s about being real. Simply put, facts about journaling for mental health by creating a mindful habit that brings peace, purpose, and personal growth.1
1
”
Journaling helps release bottled-up emotions, giving you an outlet to express thoughts without judgment. This emotional release reduces stress and creates space for positive feelings to emerge and take root. 1
Writing thoughts in a journal helps clarify what you’re feeling, offering deeper self-awareness. This clarity often brings emotional relief and strengthens your ability to understand and regulate your mood. 2
When you write about experiences consistently, your brain starts recognizing patterns in behavior or thought. This self-recognition improves emotional intelligence and helps you break free from negative thinking cycles.
Journaling daily has been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety, as it shifts focus from worry to expression. It offers a structured way to channel overwhelming thoughts into manageable ideas. 3
Expressive writing strengthens the prefrontal cortex, helping with emotional regulation and decision-making. This brain activity lowers cortisol levels, which results in less stress and a more stable mood. 4
Journaling promotes mindfulness by encouraging present-moment awareness. It slows racing thoughts, centers your attention on now, and helps you distance yourself from mental clutter, making space for calm thinking. 5
People with depression often ruminate over past regrets. Journaling helps them reframe events positively or neutrally, reducing depressive thinking and making past experiences feel less haunting and emotionally charged. 6
Keeping a journal increases self-compassion. When you write honestly and review what you’ve experienced, you’re more likely to treat yourself kindly rather than harshly, creating a healthier mental space. 7
Studies show journaling before bed can improve sleep quality. By writing down thoughts, you unload mental tension and allow your mind to relax, making it easier to fall asleep. 8
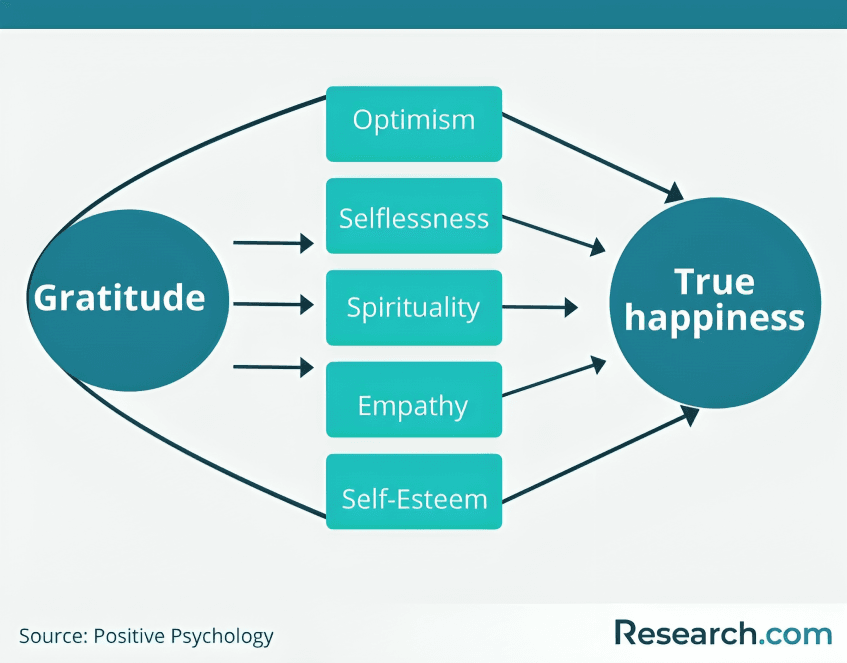
Writing about goals or daily gratitude activates positive psychology mechanisms. It rewires your brain to notice joy and progress, replacing negativity with optimism, confidence, and a stronger emotional outlook.
Tracking emotional triggers through journaling helps people manage conditions like PTSD, OCD, or panic disorder. Recognizing what causes distress empowers individuals to avoid, adapt, or respond differently over time. 9
Journaling promotes problem-solving by allowing you to break down complex situations. Writing makes abstract worries more concrete, helping you develop clearer plans and reduce feelings of helplessness or confusion. 10
Journaling fosters delayed emotional response. Instead of reacting impulsively, writing allows time to reflect, reducing the intensity of anger or sadness and replacing it with thoughtful understanding or acceptance. 11
Expressive journaling strengthens immune system functioning. Psychologists believe that reducing emotional stress allows your body to focus more on healing and less on fighting unnecessary internal anxiety or mental tension. 12
Teens who journal during tough times report improved coping skills and less emotional confusion. Writing helps them define their identity, understand emotions, and make sense of rapid life changes. 13
Therapists often recommend journaling during cognitive-behavioral therapy. It supports the therapeutic process by reinforcing new thought patterns, tracking progress, and allowing clients to continue reflecting between sessions effectively. 14

Journaling about traumatic events, especially when combined with professional help, supports emotional processing. It provides a narrative structure to overwhelming events, making them less confusing and more manageable over time.
Those struggling with chronic illness often benefit from journaling, as it allows them to process fear, frustration, or grief. Emotional clarity helps improve resilience and strengthens the mind-body connection. 15
Journaling nurtures a growth mindset. When people write about challenges and what they’ve learned, they become more resilient, seeing problems as chances to grow rather than as personal failures. 16
Daily reflection encourages accountability for mental health. Journaling reminds you to practice self-care, monitor mood patterns, and stay in tune with emotional needs, leading to better mental health management overall. 17


