“
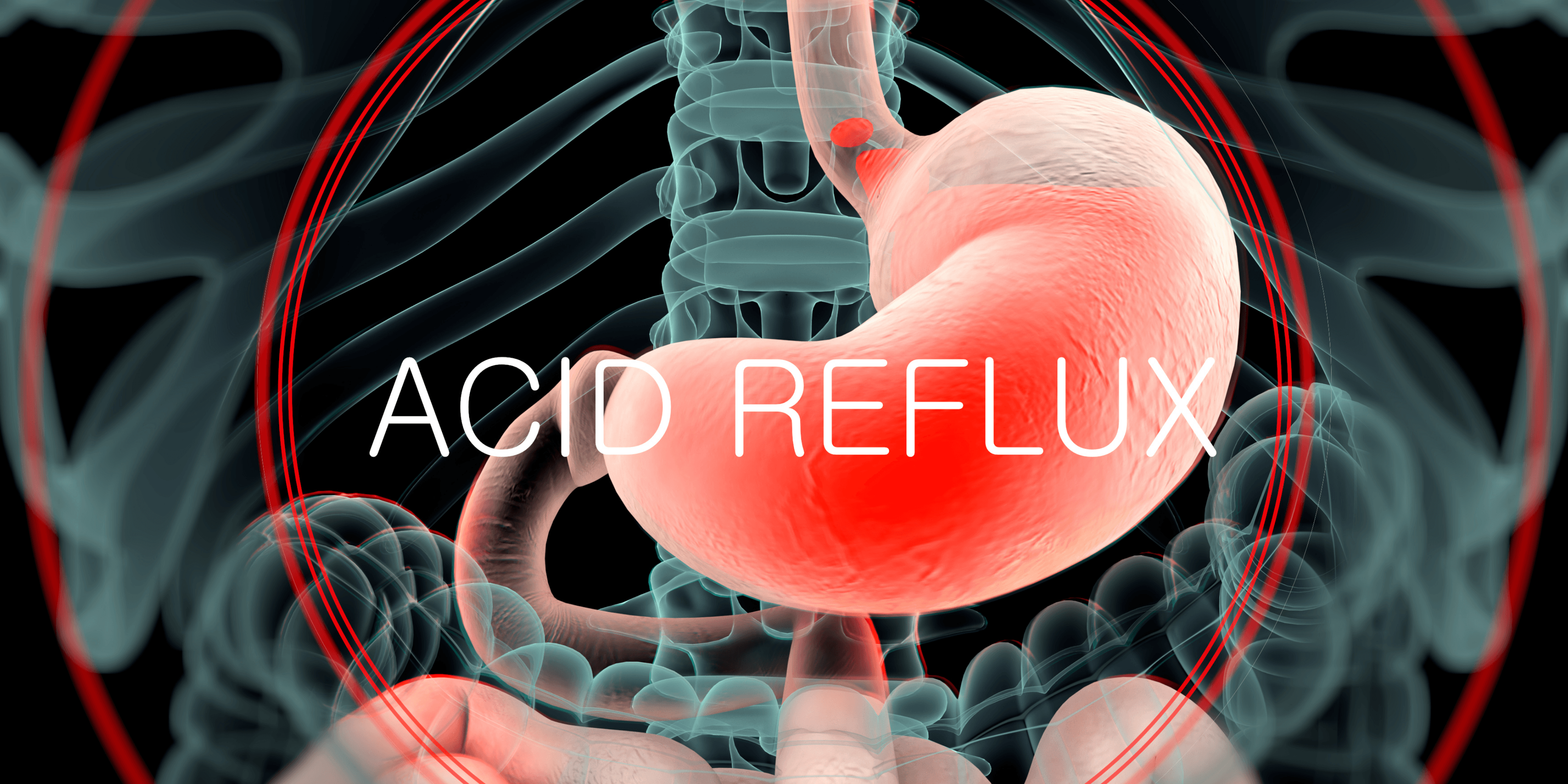
Acid reflux, medically known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing discomfort and damage. Understanding the causes and treatment of acid reflux is essential for managing symptoms and preventing complications. 1
1
”
Acid reflux occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) becomes weak or relaxes inappropriately, allowing acidic stomach contents to flow backward into the esophagus and causing heartburn symptoms. 1
Large meals increase pressure inside the stomach, which can push acid past the LES and into the esophagus, making overeating a common cause of acid reflux after heavy eating sessions. 2
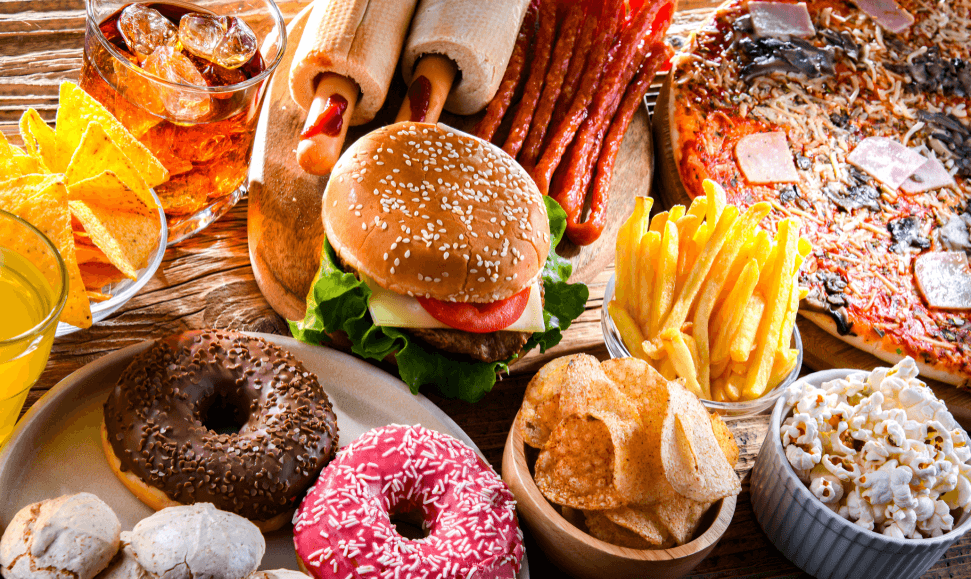

Certain foods such as spicy dishes, citrus fruits, chocolate, caffeine, and high-fat items relax the LES or increase stomach acid, triggering acid reflux symptoms in susceptible individuals.
Excess body weight, especially around the abdomen, puts additional pressure on the stomach, increasing the likelihood that acid will escape into the esophagus and cause reflux symptoms. 3
Hormonal changes during pregnancy relax the LES, while the growing uterus applies pressure on the stomach, causing frequent acid reflux in expectant mothers, especially in the later trimesters. 4
Hiatal hernia happens when part of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm, disrupting LES function and frequently leading to persistent acid reflux and discomfort in many patients. 5
Stress and anxiety can worsen acid reflux by increasing stomach acid production and causing muscle tension around the LES, which affects its ability to prevent acid backflow into the esophagus. 6
Several medications, including aspirin, ibuprofen, calcium channel blockers, and some asthma drugs, may weaken the LES or irritate the esophageal lining, leading to or worsening acid reflux symptoms. 7
Doctors commonly recommend lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, avoiding trigger foods, eating smaller meals, and quitting smoking, to effectively reduce the frequency and intensity of acid reflux episodes. 8

Elevating the head of the bed by 6 to 8 inches helps use gravity to prevent stomach acid from rising into the esophagus during sleep, significantly reducing nighttime acid reflux symptoms.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are widely prescribed because they reduce stomach acid production, allowing the esophagus to heal from irritation and providing long-term relief from acid reflux symptoms. 9
H2 receptor blockers work by decreasing acid production in the stomach and are typically used for milder acid reflux cases or in combination with other treatments for improved symptom control. 10
Herbal remedies like ginger, chamomile, and licorice root are sometimes used to soothe the digestive system and may help reduce mild acid reflux symptoms, although scientific evidence is still limited. 11
Avoiding lying down or reclining immediately after meals is important since remaining upright uses gravity to keep stomach acid from moving back into the esophagus, preventing reflux episodes. 12
Eating slowly and chewing food thoroughly aids digestion, reduces stomach pressure, and minimizes acid production, which helps lower the chance of acid reflux occurring after meals. 13

Drinking adequate water throughout the day can help dilute stomach acid and flush it back into the stomach, which reduces acid reflux frequency and soothes the esophageal lining.
Wearing tight clothing around the waist or abdomen increases pressure on the stomach, promoting acid reflux; choosing looser clothes helps reduce this external pressure and symptom risk. 14
Incorporating alkaline foods, such as bananas, melons, and oatmeal, may help neutralize stomach acid naturally and ease acid reflux symptoms by balancing the stomach’s pH level. 15
Philosopher Hippocrates, over two millennia ago, recognized that diet and lifestyle have a profound effect on digestion and health, laying early groundwork for understanding conditions like acid reflux. 16
Modern doctors emphasize combining medication, dietary adjustments, and behavioral changes as the most effective approach to treating acid reflux and improving patients’ quality of life sustainably.17


