“
Architecture in the Neolithic Era marks a pivotal transition in human history. As societies shifted from nomadic lifestyles to settled agricultural practices, the demand for permanent structures increased dramatically. In this blog, we will explore 20 fascinating facts about architecture in the Neolithic Era, showcasing how these early innovations laid the groundwork for generations to come.1
”
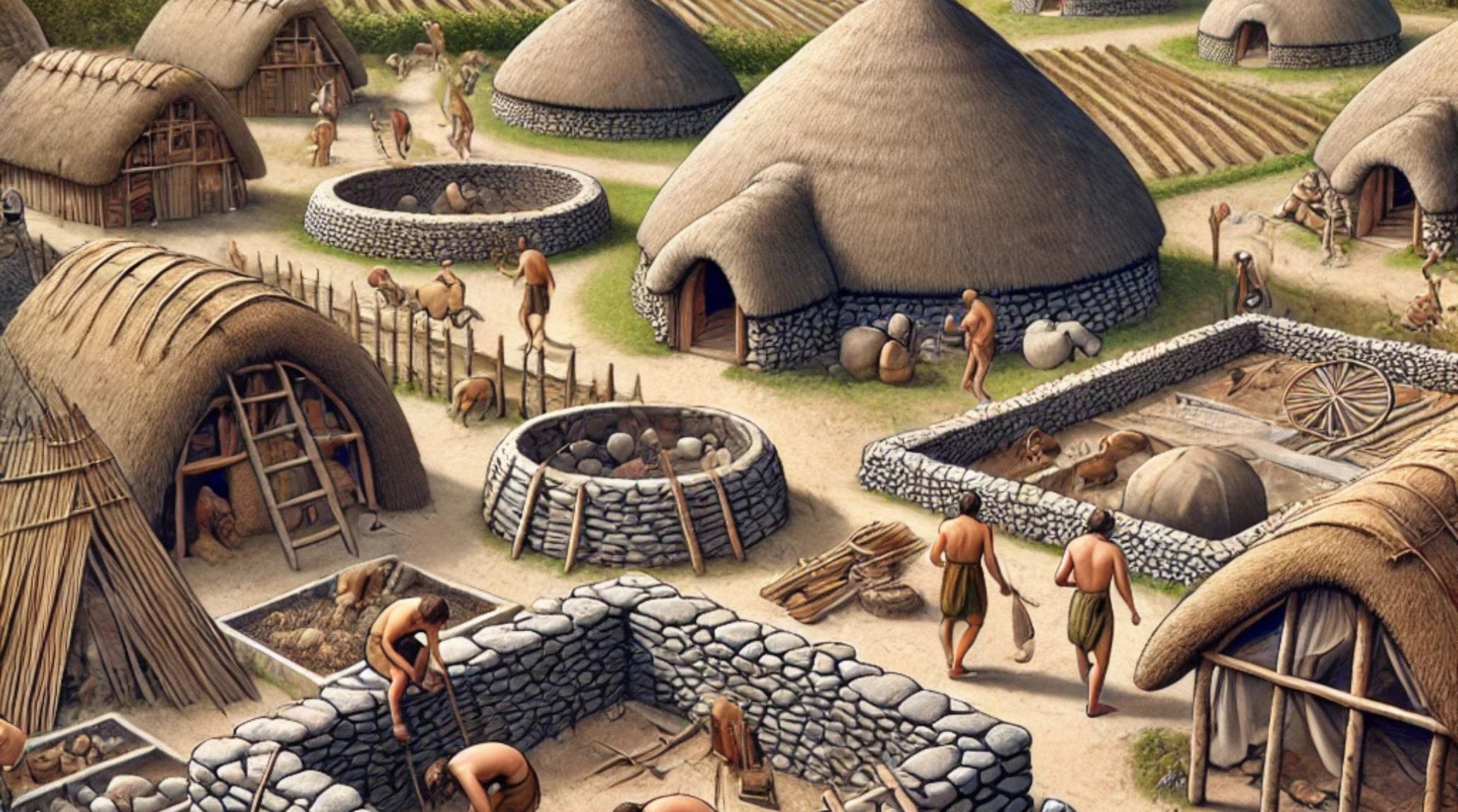
Neolithic architecture marked a shift from temporary shelters to permanent homes, allowing communities to settle, cultivate land, and foster social interactions, shaping future civilizations.1
Mud bricks became essential for building durable homes. Their excellent insulation properties provided warmth, showcasing early builders' resourcefulness in using local materials for comfortable living.2
Megalithic structures, like Stonehenge, served ceremonial and astronomical purposes. These impressive sites reflected the Neolithic focus on rituals, connecting communities to their beliefs and the cosmos.3
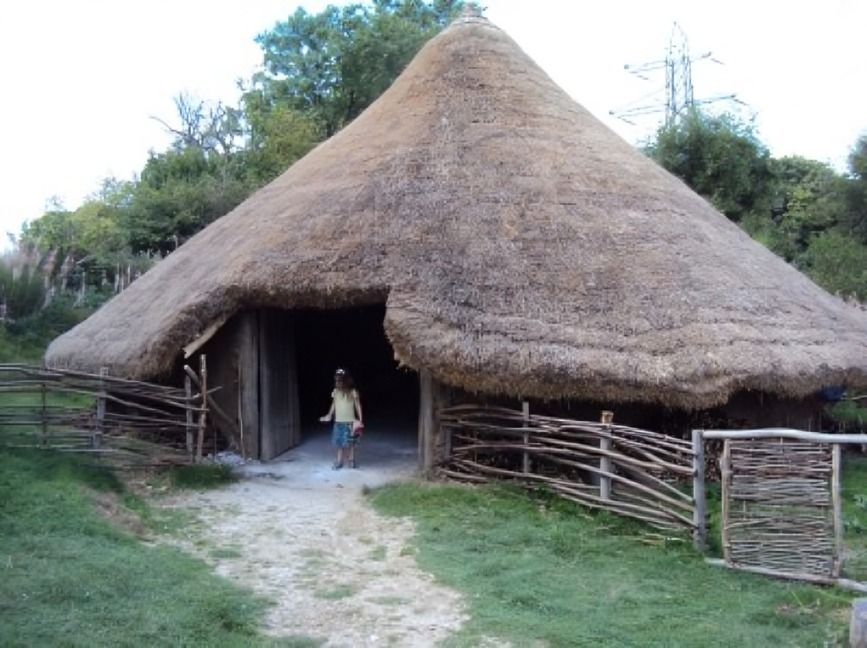

Round houses were commonly found in Neolithic villages. Their efficient and spacious design encouraged communal living, fostering strong family bonds and cooperation among inhabitants while maximizing available space and resources effectively.
Thatch roofs made from grass or reeds protected Neolithic dwellings from rain. This practical roofing method demonstrated early builders' understanding of environmental adaptation and local resources.4
Neolithic village layouts revealed social hierarchies. Larger homes belonged to influential families, indicating the emergence of social stratification in these early agricultural societies.5
Post-and-beam construction techniques showcased Neolithic builders' ingenuity. These methods enabled larger, sturdier structures, paving the way for future architectural advancements in society.6
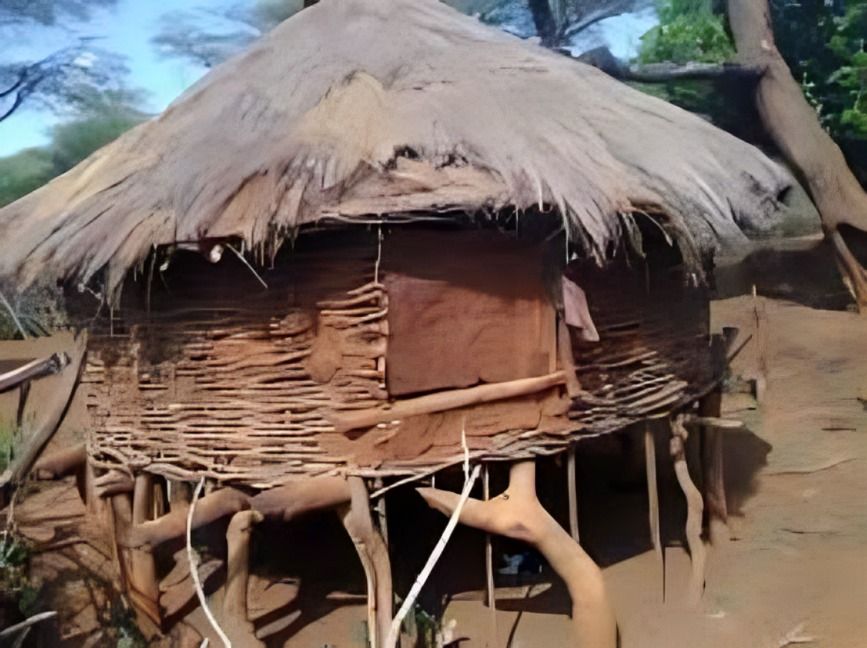

Storage facilities, such as granaries, played a vital role in preserving surplus food. These architectural innovations enabled Neolithic communities to thrive during harsh seasons, showcasing their impressive early resource management and planning skills for sustainability.
Interconnected homes, seen in sites like Çatalhöyük, encouraged communal living. This design promoted social interaction, cooperation, and shared activities among early inhabitants, strengthening community ties.7
Decorative painted pottery adorned Neolithic homes, revealing artistic expression and cultural identity. These elements reflected the aesthetic values and spiritual beliefs of Neolithic people.8
Stone walls provided protection for Neolithic settlements. These fortifications highlighted early defensive strategies and the significance of safety in the evolving complexities of human communities.9
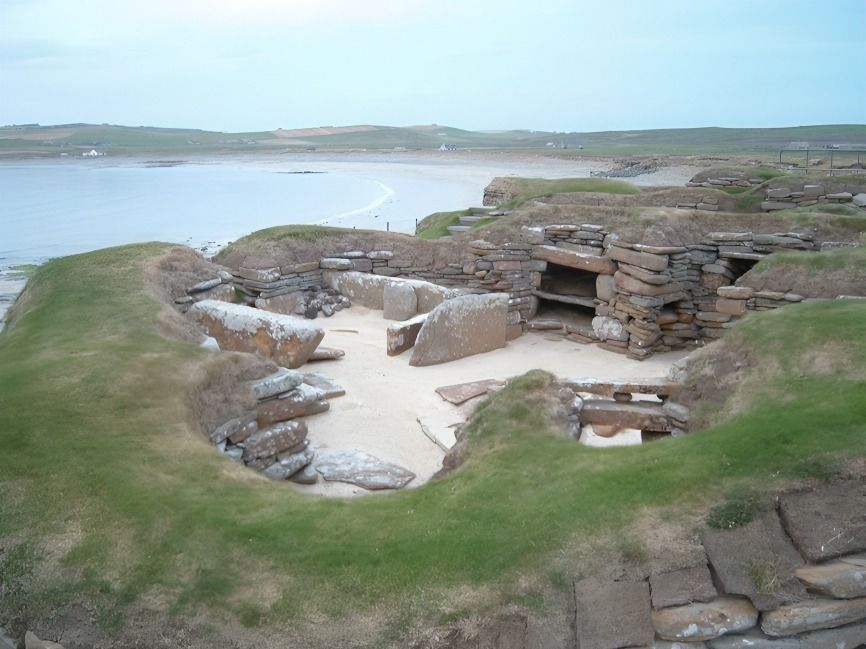

Sacred spaces, including shrines, highlighted the religious significance of Neolithic architecture. These areas functioned as focal points for communal worship, emphasizing the deep spiritual connections and beliefs that existed within early societies.
Many Neolithic structures aligned with astronomical events, capturing solstice light. This orientation illustrated the importance of celestial bodies in shaping cultural practices and communal life.10
Burial mounds, or tumuli, became significant architectural features. Serving as resting places for prominent individuals, they reflected cultural importance of ancestor veneration in early societies.11
Architectural styles varied by region, adapting to local environments. From stilt houses to stone structures, Neolithic builders showcased creativity and resourcefulness in their designs.12
Communal spaces, like meeting halls, fostered communication and decision-making in Neolithic societies. These gathering places reinforced social cohesion, enabling collaboration and planning within agricultural communities.13
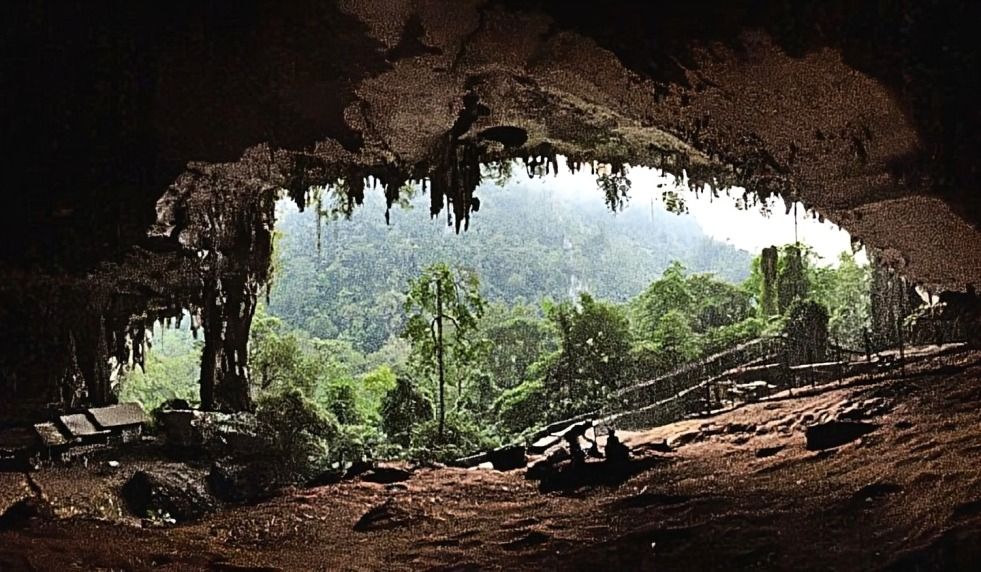

Natural features, like caves, were cleverly integrated into Neolithic settlements. This combination provided essential protection and aesthetic appeal, showcasing early builders' ability to harmonize architecture with their surroundings.
Innovations in Neolithic architecture laid the groundwork for future civilizations. The knowledge gained during this era influenced urban planning and monumental structures for millennia.14
Environmental awareness influenced Neolithic builders' site selections. Choosing locations that maximized sunlight and resources reflected their understanding of nature’s role in sustainable living.15
Neolithic architecture's legacy continues to inspire modern designs. Sustainable building practices today echo early principles, showcasing the lasting impact of the Neolithic Era on contemporary society.16