“
Ceramics are more than just decorative pottery; they are an essential part of technology and culture. Throughout history, ceramics have been utilized for a wide range of purposes, from ancient art to modern engineering. This article presents 20 amazing facts about ceramics that showcase their remarkable versatility and enduring significance.1
1
”
Ceramics have been used by humans for over 24,000 years, with some of the earliest examples found in ancient pottery and sculptures. Early civilizations, such as the Egyptians and Greeks, utilized ceramics for artistic and functional purposes.1
Some orthopedic hip replacements use ceramic prostheses for improved bone integration. Synthetic hydroxyapatite, mimicking the natural mineral in bone, is formed into ceramics from biological and chemical sources.
Ceramic knife blades remain sharp much longer than steel but are more brittle. They can snap or chip if dropped on a hard surface. Despite this, their edge retention makes them ideal for precise cutting tasks. 2
Ceramics are broadly categorized into four main types: earthenware, stoneware, porcelain, and bone china. Each type has different properties, such as porosity, hardness, and durability, making them suitable for various applications. 3
One of the most remarkable properties of ceramics is their ability to withstand extreme temperatures, with melting points often exceeding 2,000°C. This makes ceramics ideal for use in high-temperature environments.4
The most expensive porcelain tableware, a Ming Dynasty "Chicken Cup" bowl, was sold in Hong Kong in 2015 for $36 million. Depicting a rooster, chicken, and chick, the relic is approximately 500 years old. 5
Ceramics are excellent electrical insulators, which is why they are widely used in electronics. Materials like alumina and zirconia are commonly used for insulating components in semiconductors, circuit boards, and transformers. 6
Ceramics are highly resistant to most chemicals, including acids and alkalis, making them ideal for use in corrosive environments. This property is critical in industries such as chemical processing, where ceramic-lined pipes and tanks. 7
Certain ceramics, like zirconia and bioglass, are used in medical applications due to their biocompatibility. These materials are employed in dental implants, joint replacements, and bone scaffolding. 8
Advanced ceramics, such as silicon carbide and alumina, are engineered for high-performance applications. They are used in aerospace, automotive, and military industries for their exceptional hardness and resistance9
One of the most common uses of ceramics is in the production of tiles for flooring and walls. Ceramic tiles are popular for their durability, water resistance, and ease of cleaning, making them ideal for bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor spaces. 10
Ceramic materials are excellent thermal insulators due to their low thermal conductivity. This makes them useful in applications such as thermal barrier coatings in jet engines and insulating bricks in high-temperature furnaces. 11
Certain ceramics, like lead zirconate titanate (PZT), exhibit piezoelectric properties, meaning they can generate an electrical charge under mechanical stress.12
Ceramics are often glazed to create a smooth, colorful surface that is both decorative and protective. Glazing not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of pottery and tiles but also makes the material more resistant to water and stains. 13
Ceramics play a critical role in space exploration, particularly in the form of heat-resistant tiles used on spacecraft like the Space Shuttle. These ceramic tiles protect the spacecraft from the intense heat generated during re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere.14
Ceramic materials are often more environmentally friendly than plastics and metals. They are made from abundant natural materials like clay and are non-toxic. 15
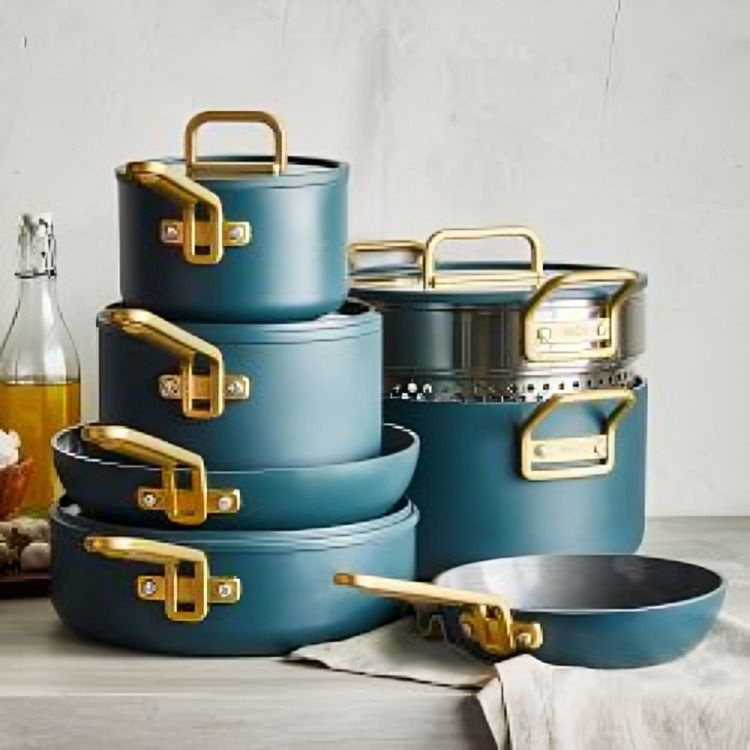

Ceramic cookware, such as casseroles and baking dishes, is favored for its ability to evenly distribute heat and retain temperature. Additionally, ceramic coatings on cookware provide a non-stick surface.
Ceramics can be engineered to have specific acoustic properties, making them ideal for use in musical instruments and soundproofing materials. Ceramic speakers and components are prized for their ability to deliver clear, high-quality sound. 16
In construction, ceramics are used in bricks, roofing tiles, and sewer pipes due to their strength, durability, and resistance to weathering. These materials have been used in building for centuries, from ancient structures to modern-day architecture. 17
Nanotechnology has advanced the field of ceramics, leading to the development of nanoceramics with enhanced properties. These materials exhibit superior strength, flexibility, and wear resistance, making them useful in cutting-edge technologies. 18


